Finned tube heat exchangers are widely used in industries requiring efficient heat transfer between fluids. They stand out for their ability to increase heat transfer rates through the addition of “fins” around the tubing, making them highly effective and versatile. This guide covers everything you need to know about finned tube heat exchangers, including how they work, their advantages, types, applications, and why they’re preferred for various industrial uses.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
To fully understand finned tube heat exchangers, it’s essential to know what a heat exchanger is. A heat exchanger is a device that facilitates the transfer of heat between two or more fluids (liquids or gases) without them mixing. The fluids are separated by a solid wall, usually metal, which enables heat transfer through conduction. Heat exchangers are critical components in industries like HVAC, chemical processing, power generation, refrigeration, and more. They improve efficiency, reduce energy costs, and allow precise temperature control in processes requiring thermal management.
What is a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger?
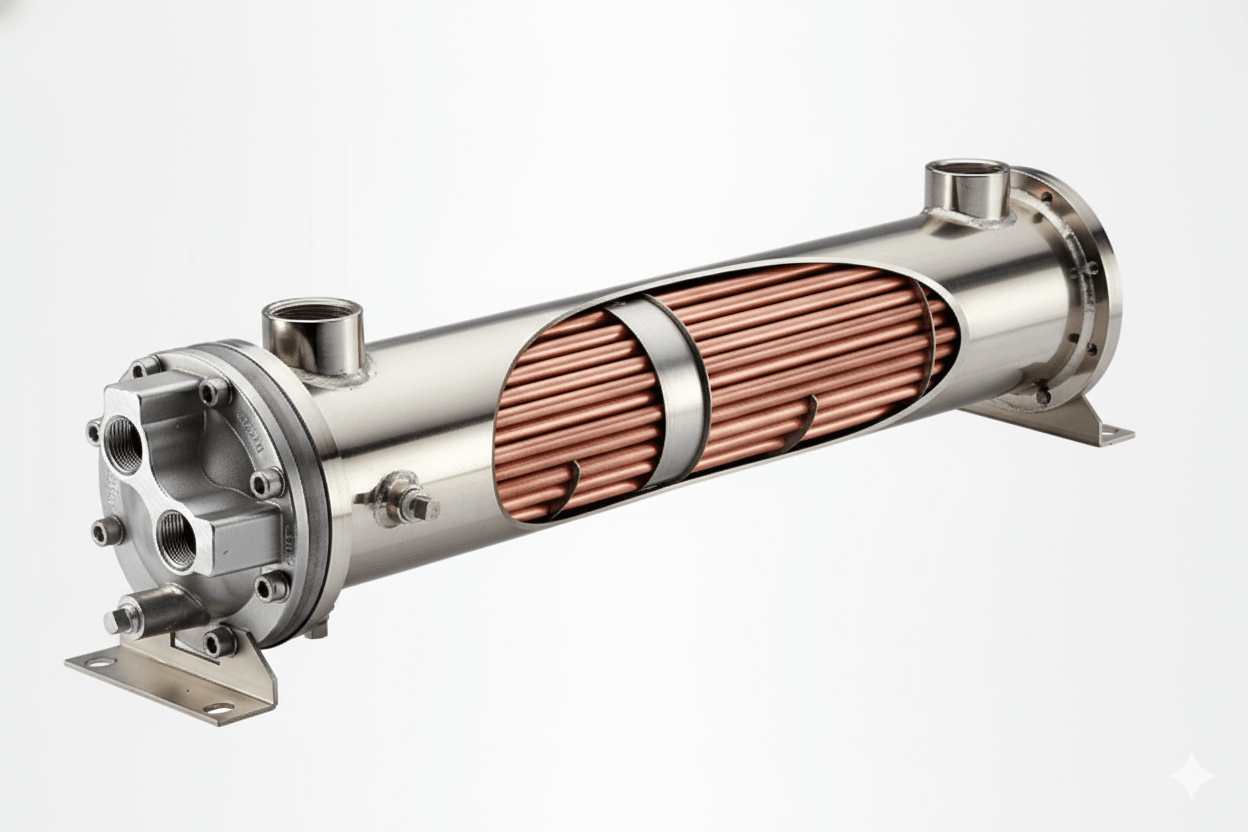
A finned tube heat exchanger is a specific type of heat exchanger that enhances the heat transfer surface area using extended fins attached to the outside of the tubes. These fins are typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or copper. The increased surface area provided by the fins allows for a higher rate of heat transfer from the fluid inside the tube to the surrounding fluid. By boosting the heat exchange efficiency, finned tube heat exchangers enable smaller, more compact designs while maintaining high performance.
How Do Finned Tube Heat Exchangers Work?
The operating principle of a finned tube heat exchanger relies on conduction and convection. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Fluid 1 (Hot Fluid): This fluid flows through the inside of the finned tube.
- Fins: These fins surround the outside of the tube, increasing the heat transfer surface area.
- Fluid 2 (Coolant): The secondary fluid flows over the fins on the outside, picking up or dissipating heat.
The increased surface area from the fins improves the overall heat transfer rate between the two fluids. In short, the fins conduct heat from the hot fluid inside the tube, while convection removes this heat from the outer fin surface as the second fluid flows over it.
Benefits of Using Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- Enhanced Efficiency: Fins increase the available surface area for heat transfer, resulting in a more efficient heat exchange process.
- Space-Saving: Since they require less space to achieve desired heat transfer levels, they allow for more compact designs, which is crucial in applications with space constraints.
- Energy Savings: Increased efficiency leads to reduced energy requirements, translating to lower operational costs.
- Versatility: Finned tube heat exchangers can operate in a range of environments, from high to low temperatures, making them suitable for multiple industries.
Key Applications of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers are essential in various industries, primarily due to their efficiency and flexibility. Here are some common applications:
- HVAC Systems: They are used in air conditioning and heating systems for controlling indoor air temperature.
- Power Generation: Finned tube heat exchangers transfer heat in cooling towers and condensers, which is vital in power plants.
- Refrigeration: They enable heat removal in refrigeration systems, helping to maintain low temperatures in commercial and industrial freezers.
- Chemical Processing: In processes requiring precise temperature control, finned tube heat exchangers provide reliable heat transfer.
- Automotive: Many automotive systems, including radiators and oil coolers, rely on finned tube heat exchangers to dissipate heat.
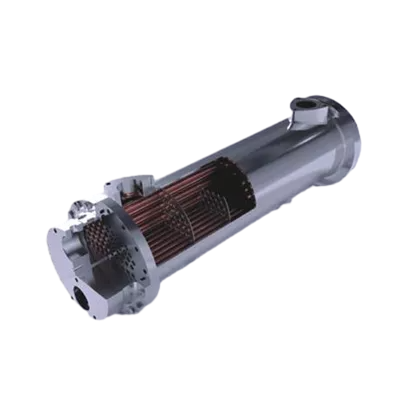

Types of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers come in several types, each suited for different requirements. Here are the most common types:
- Extruded Fin Tubes: These are made by extruding aluminum fins onto a tube, creating a strong bond between the fin and tube for better heat transfer. These are widely used in industries requiring durable, high-performance solutions.
- L-Foot Finned Tubes: These have fins wrapped around the tube in an L-shape, providing good thermal contact while reducing the risk of fin detachment. This design is commonly found in applications where high heat transfer rates are required.
- Embedded Finned Tubes: In this design, fins are embedded into the tube surface for maximum heat transfer efficiency and durability. This type is ideal for demanding environments with high temperatures.
- Welded Finned Tubes: Here, fins are welded onto the tubes, resulting in a solid connection. These are often used in high-pressure applications where durability is critical.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger
Choosing the right finned tube heat exchanger involves considering the requirements of your specific application:
- Material: Select a material that offers high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Aluminum and copper are common choices, while stainless steel is preferred for corrosive environments.
- Fin Density: Higher fin density increases the surface area and heat transfer rate but may also result in higher pressure drops. Balance fin density based on the required heat transfer rate and pressure tolerance.
- Tube Design: Consider the tube diameter and length based on space limitations and performance requirements.
- Operating Conditions: Understand the temperature and pressure conditions your heat exchanger will face. Different types of finned tube heat exchangers are suited for various environments, so match the design to the conditions of use.
- Maintenance: Choose a design that allows easy cleaning and maintenance, especially in environments prone to dust and debris accumulation, which can block fins and reduce efficiency.
Why Finned Tube Heat Exchangers are the Preferred Choice
Finned tube heat exchangers are preferred in many industries due to their adaptability, durability, and efficiency. Compared to other types of heat exchangers, they provide a compact, energy-efficient solution capable of handling large heat loads. Their design can be customized with different fin types, densities, and materials, ensuring compatibility with specific needs.
How to Maximize the Performance of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
To get the most out of a finned tube heat exchanger, regular maintenance is essential. Dust and dirt can accumulate on the fins, which reduces the available heat transfer surface area and lowers efficiency. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the fins and tubes regularly to prevent dust buildup. Compressed air or gentle brushing is often effective.
- Inspect for Corrosion: Corrosion on fins or tubes can reduce performance, especially in humid or chemically reactive environments.
- Monitor for Pressure Drops: Significant pressure drops can indicate blockages or reduced heat transfer efficiency. Address these issues promptly to maintain performance.
Conclusion:Finned tube heat exchangers are powerful, efficient, and versatile tools for industries that require effective heat transfer. By leveraging the increased surface area provided by fins, these heat exchangers maximize the heat exchange rate while saving space and energy. From HVAC systems to automotive radiators and industrial refrigeration, finned tube heat exchangers provide reliable and cost-effective thermal management solutions for a wide range of applications. Selecting the right type and maintaining it properly can ensure optimal performance and longevity, making them a valuable asset in thermal management systems across industries.