In the world of heat exchangers, two of the most commonly used designs are shell-and-tube and finned tube heat exchangers. Each of these types has unique characteristics, applications, and benefits, making them suitable for different industrial needs. This guide will explore the differences between shell-and-tube and finned tube heat exchangers, focusing on design, functionality, efficiency, and applications.
“Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are ideal for high-pressure applications and heavy-duty industrial use, while finned tube heat exchangers offer compact design and high efficiency, making them suitable for systems with space limitations.” Knowing the differences can help you select the right heat exchanger for your specific requirements.
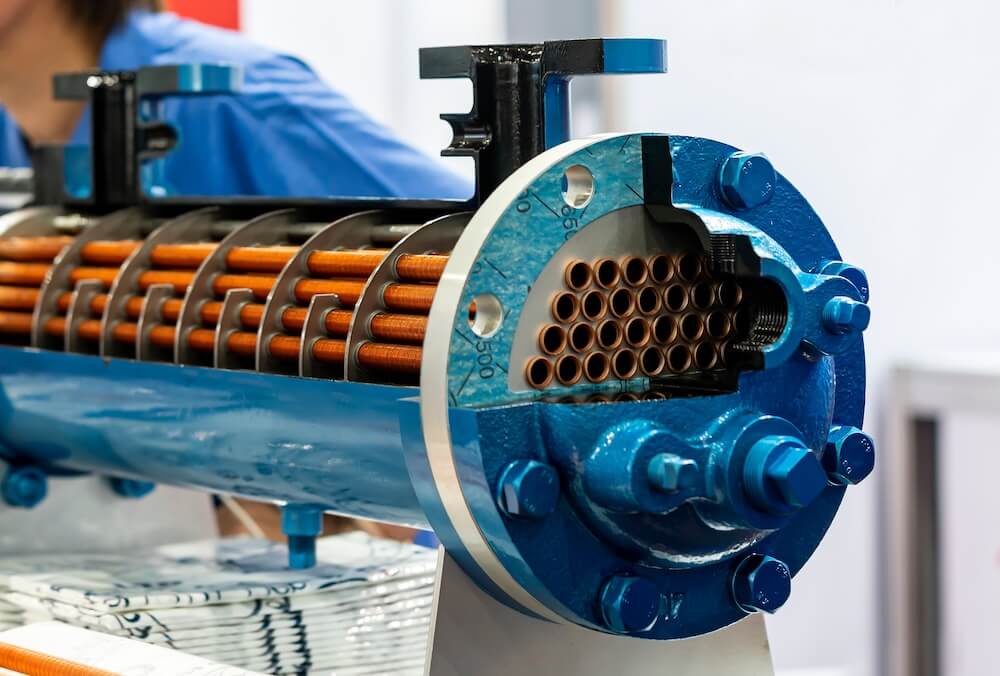
What is a Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger?
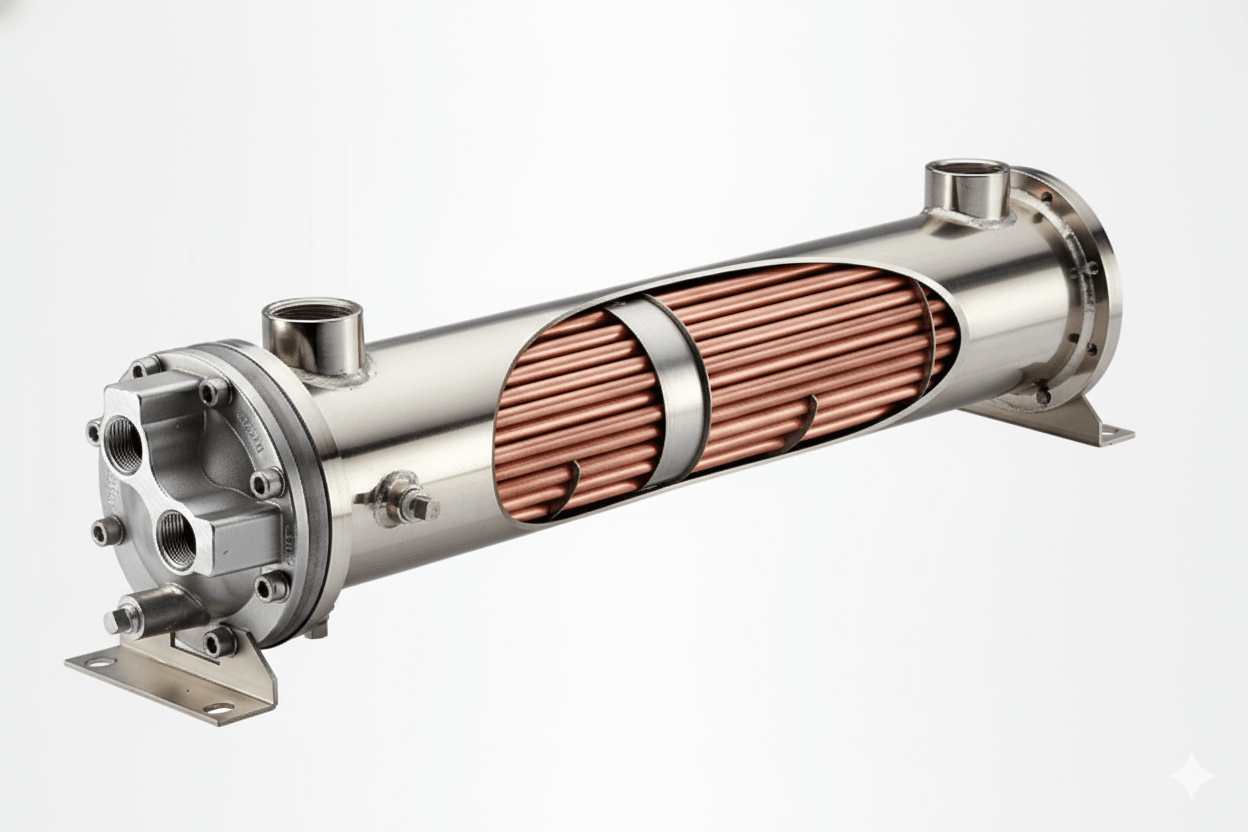
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger consists of a bundle of tubes enclosed in a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, while another fluid flows around the tubes within the shell, separated by the tube walls. Heat transfer occurs as these fluids pass each other, with one fluid typically cooling while the other heats up. This design is widely used in industries requiring high-pressure handling and efficient heat exchange, such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing.
Key Characteristics of Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers
- High Durability: Built for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, shell-and-tube heat exchangers are highly durable.
- Easy to Maintain: The tube bundle in shell-and-tube heat exchangers is often removable, which allows for easier maintenance, cleaning, and replacement.
- Ideal for Large-Scale Applications: Due to their robust design and ability to handle large volumes, shell-and-tube exchangers are commonly used in industrial settings with heavy-duty requirements.
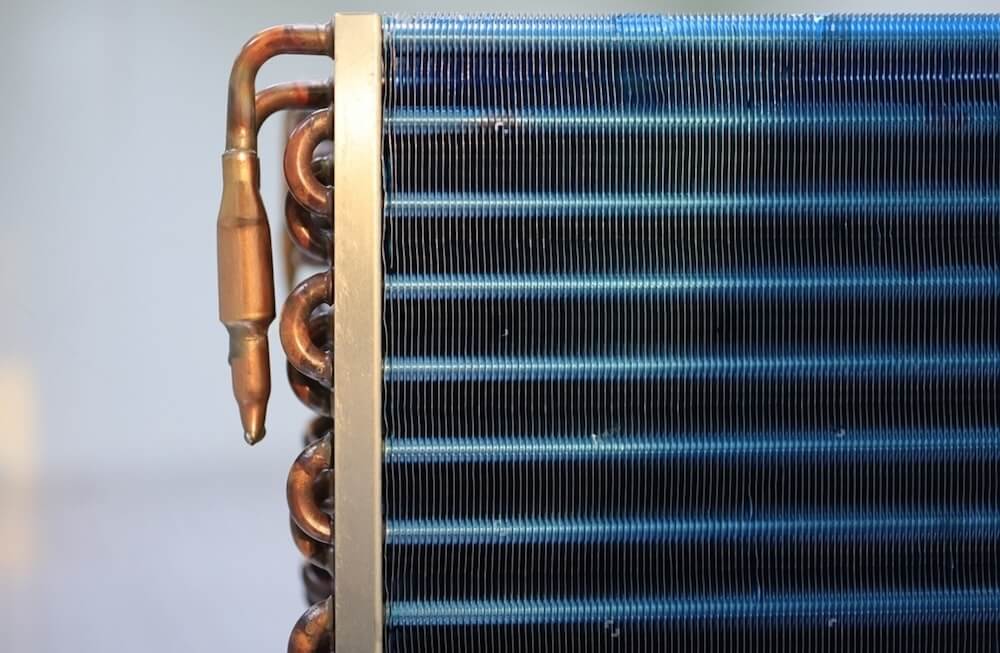
What is a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger?
A finned tube heat exchanger, on the other hand, consists of tubes with fins attached to their outer or inner surfaces. These fins significantly increase the surface area, which enhances the rate of heat transfer. The finned design enables these heat exchangers to be compact while still achieving efficient heat exchange, making them ideal for space-limited applications. Finned tubes can have fins on one or both sides (internal and external), which further increases the efficiency by maximizing the surface area in contact with the fluids.
Key Characteristics of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- Compact and Lightweight: Finned tube heat exchangers are generally smaller and more compact, saving space while maintaining high efficiency.
- Increased Heat Transfer Efficiency: With fins on the tubes, these exchangers provide more surface area for heat transfer, enabling faster and more effective temperature control.
- Suitable for Low- to Medium-Pressure Applications: Finned tube exchangers are commonly used in applications that don’t involve extremely high pressures or temperatures, such as HVAC, refrigeration, and automotive cooling systems.
Comparing Shell-and-Tube and Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Although both types of heat exchangers aim to transfer heat between two fluids efficiently, shell-and-tube and finned tube heat exchangers differ significantly in terms of design, heat transfer efficiency, and ideal use cases. Here’s how they compare across several key aspects:
1. Design and Construction
The fundamental design of these two heat exchangers is quite different, leading to distinct benefits and limitations.
- Shell-and-Tube Design: Shell-and-tube heat exchangers have a simple yet robust design. They consist of a series of straight or U-shaped tubes inside a large cylindrical shell. This design is built for durability, allowing it to handle high pressures and large volumes of fluid, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Finned Tube Design: Finned tube heat exchangers are constructed with tubes that have fins attached to increase surface area. These fins can be external, internal, or both, and are typically made of aluminum or copper. The increased surface area of finned tubes allows for high heat transfer rates in a smaller form, ideal for compact systems.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency
Both shell-and-tube and finned tube exchangers are efficient, but they achieve heat transfer in different ways and are optimized for different kinds of efficiency.
- Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers: Shell-and-tube exchangers can handle large flow rates and allow for significant heat transfer, but they may require more space to achieve the same efficiency level as a finned tube exchanger. They work best when there is a need for a high volume of fluid transfer and when the fluids have substantial temperature differences.
- Finned Tube Heat Exchangers: Finned tubes excel at maximizing heat transfer in a compact space due to their increased surface area. The fins allow for faster heat exchange, making them highly efficient even at low to moderate flow rates. This design is optimal for systems that require high efficiency in smaller installations, such as HVAC systems or automotive radiators.
3. Pressure and Temperature Tolerance
Tolerance to high pressure and temperature varies between these two types of heat exchangers, making each suitable for different industrial applications.
- Shell-and-Tube Exchangers: These exchangers are known for their resilience in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. They are commonly used in industrial applications where extreme conditions are a factor, as they can withstand intense pressures without compromising performance.
- Finned Tube Exchangers: Finned tube heat exchangers are typically more suited for moderate pressure and temperature applications. While they can handle some degree of pressure, they are less robust than shell-and-tube exchangers, making them ideal for applications where space and efficiency are prioritized over pressure tolerance.
4. Maintenance and Cleaning
Ease of maintenance is crucial for long-term performance, especially in industrial settings where equipment needs to be regularly cleaned and inspected.
- Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers: These are relatively easier to maintain due to their design. The tube bundle in many shell-and-tube exchangers can be removed for cleaning or replacement, allowing for effective maintenance in industrial environments where fouling and scaling may occur frequently.
- Finned Tube Heat Exchangers: Maintenance of finned tube exchangers can be more challenging, as dirt, dust, and other particles can get trapped in the fins, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Regular cleaning of the fins is necessary to maintain performance, especially in applications like HVAC where air quality is critical.
5. Space and Weight Considerations
Space and weight can be important factors depending on the application, and each type of heat exchanger has its strengths and weaknesses in this regard.
- Shell-and-Tube Exchangers: Due to their cylindrical shape and lack of fins, shell-and-tube exchangers are bulkier and require more space for installation. They are better suited for large, industrial installations where space is not a primary constraint.
- Finned Tube Exchangers: With their compact, lightweight design, finned tube exchangers are ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in HVAC systems, automotive engines, and portable cooling systems. The finned design achieves high efficiency without requiring large amounts of space.
Applications of Shell-and-Tube vs. Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Both types of heat exchangers have unique applications based on their design and capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of where each type excels:
1. Shell-and-Tube Applications
- Oil and Gas Processing: Used extensively in oil refineries and gas processing plants, where high pressures and temperatures are common.
- Power Generation: Employed in power plants where the heat exchanger needs to handle large volumes and extreme conditions.
- Chemical Processing: Ideal for chemical plants that require durable and efficient heat exchange for continuous operations.
2. Finned Tube Applications
- HVAC and Refrigeration: Finned tubes are commonly used in HVAC and refrigeration systems where compact, efficient cooling is essential.
- Automotive and Engine Cooling: Their lightweight and efficient design makes them suitable for automotive radiators and other cooling applications in vehicles.
- Aerospace and Compact Systems: Due to their compact size, finned tube exchangers are often used in aerospace applications and small cooling systems where space is limited.
Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger for Your Needs
When deciding between a shell-and-tube and a finned tube heat exchanger, consider the specific requirements of your application:
- For High Pressure and Heavy-Duty Applications: Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. They are better suited for industrial applications requiring durability and large-scale heat transfer.
- For Compact, Efficient Cooling: Finned tube exchangers are optimal for applications where space is limited but efficient heat transfer is essential. These exchangers perform well in moderate-pressure environments, making them suitable for HVAC, automotive, and small-scale cooling systems.
Final Thoughts
Shell-and-tube and finned tube heat exchangers both play critical roles in heat transfer across different industries. By understanding their distinct advantages and limitations, you can select the type that best meets your system’s requirements.
Summary: Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are robust and ideal for high-pressure applications, while finned tube exchangers offer a compact, efficient solution for low- to medium-pressure environments. Selecting the right type of heat exchanger ensures optimal performance and longevity based on your unique cooling needs.
With the right choice, you can achieve efficient, reliable heat transfer in your application, whether it requires industrial-scale durability or compact, high-efficiency cooling.