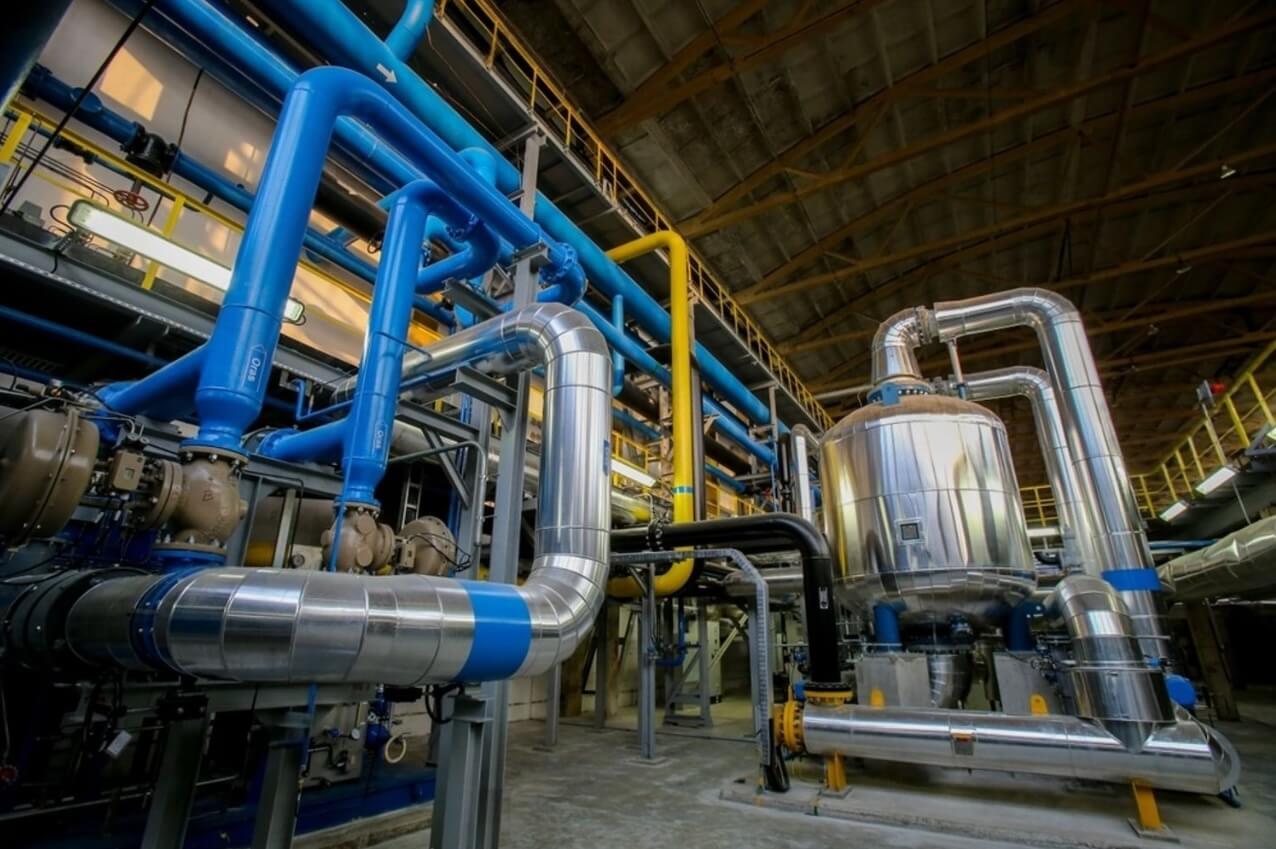
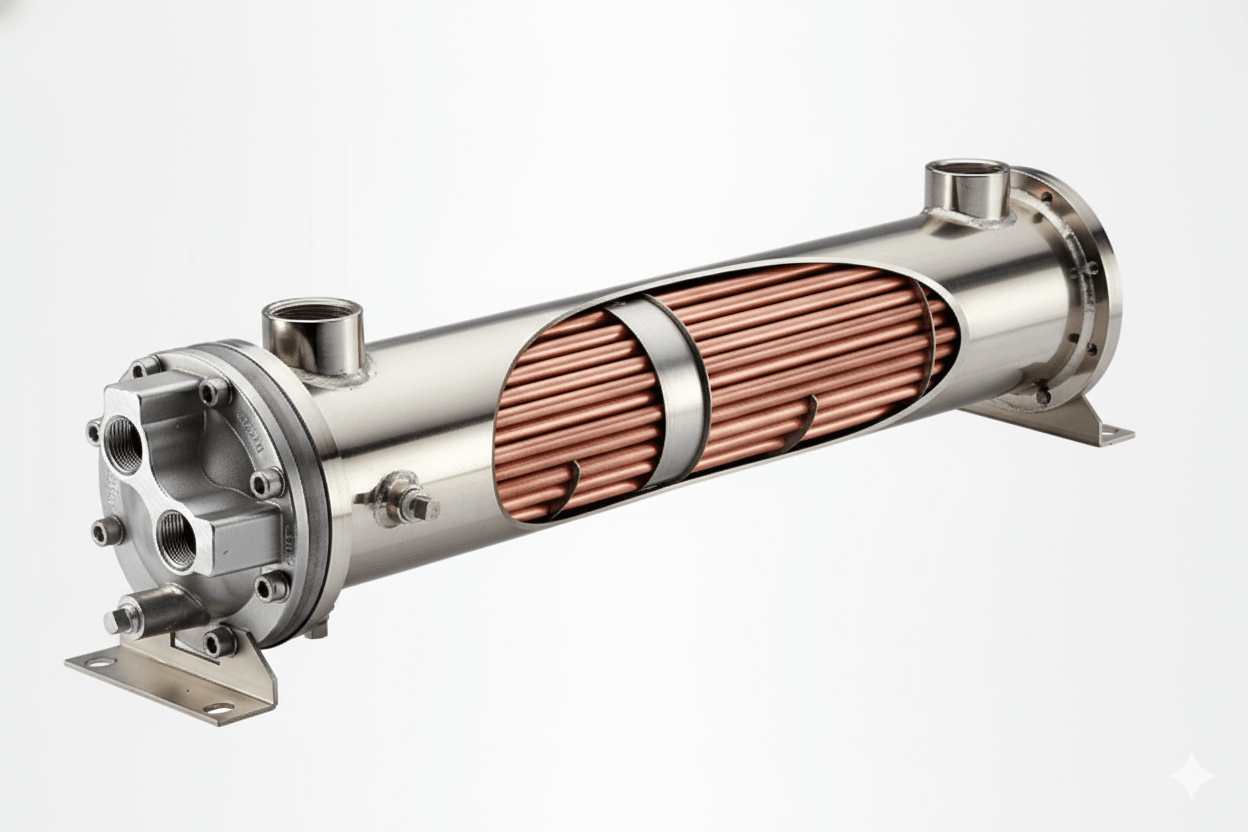
In industrial HVAC systems, the efficiency of air-to-liquid heat transfer is paramount. It determines not only climate control effectiveness but also operational costs. At the heart of this process are finned tube coils, which are specially designed heat exchangers. These coils transfer heat between a fluid, like water or refrigerant, and the surrounding air. While their basic function seems simple, a coil’s real-world performance is a complex interplay of design, maintenance, and system integration. This article delves into how to optimize these critical components using advanced fin designs and smart operational strategies.
The Hidden Cost of Dirty Coils: Calculating Energy Penalties and System Efficiency Losses
Over time, a coil’s surface can become coated in dirt, dust, and other airborne particles—a process known as fouling. This seemingly harmless buildup has a hidden cost. It acts as an insulator, drastically reducing the coil’s ability to transfer heat. This forces the HVAC system to work harder and run longer to achieve the desired temperature, leading to a direct increase in energy consumption. Calculating these energy penalties involves comparing a system’s power consumption with clean coils versus its consumption with fouled ones. This analysis often reveals that the system efficiency losses are significant, making regular maintenance a sound financial decision.
To combat the issues of fouling and wear, facility managers need a proactive approach. A well-defined preventive maintenance schedule is key. This schedule should include regular visual inspections, pressure drop checks, and cleaning sessions. For light dirt, a simple brush or compressed air may suffice. For heavier buildup, a gentle pressure washer with a coil-safe cleaning solution might be necessary. By following a consistent maintenance plan, facility managers can ensure their finned tube coils operate at peak efficiency and avoid costly emergency repairs.
Coil Selection Parameters: Balancing Heat Transfer, Pressure Drop and System Efficiency
Choosing the right coil for a specific application requires careful consideration of several key coil selection parameters. The goal is to find the perfect balance between high heat transfer capacity, minimal pressure drop, and overall system efficiency. A coil with a high fin density might offer excellent heat transfer but could also restrict airflow, forcing the fan to work harder. Conversely, a coil with low fin density might have a low pressure drop but a poor heat transfer rate. Engineers must use data and calculations to choose a coil that provides the required performance without overburdening other system components.
The easiest way to keep coils clean is to prevent contaminants from reaching them in the first place. Air filtration strategies are the primary defense. Using high-efficiency air filters, such as MERV-rated filters, can capture a wide range of airborne particles, including fine dust and pollen. Implementing a two-stage filtration system, with a coarser filter followed by a finer one, can provide even better protection. This proactive approach helps to extend finned tube coil life and allows the system to maintain peak performance with minimal cleaning.
Industrial Process Heating: Troubleshooting Common Finned Tube Coil Performance Issues
In industrial process heating, finned tube coils often face extreme temperatures and demanding conditions. Troubleshooting common performance issues requires a systematic approach. If a coil isn’t heating or cooling as expected, the first steps are to check for proper fluid flow, look for air or vapor locks, and inspect for physical damage to the fins. Other common issues include improper temperature set points, leaks in the fluid circuit, and external factors like ambient temperature or airflow blockages.
When cleaning is necessary, choosing the right method is vital. A comparative analysis of cleaning methods for industrial grade finned tube heat exchangers shows a range of options. Mechanical cleaning using brushes or scrapers is suitable for heavy, dry deposits. Chemical cleaning using foaming coil cleaners can dissolve stubborn grime and grease. In some cases, high-pressure water jets or steam cleaning can be effective, but care must be taken to avoid damaging the delicate fins. The best method depends on the type of fouling and the coil’s material.
Beyond BTU Ratings: Understanding the Real-World Performance of Heat Transfer Coils
A coil’s stated BTU rating is a theoretical value based on ideal conditions. Understanding the real-world performance of heat transfer coils means looking at more than just this number. Factors like ambient temperature, relative humidity, air velocity, and the presence of contaminants all affect how a coil performs in an actual installation. A coil may have a high BTU rating, but if it’s placed in a hot, humid environment with restricted airflow, its real-world performance will be significantly lower. This is why a holistic system analysis is crucial.
The design of a finned tube coil is highly specialized. Fin spacing and material selection are two of the most critical design considerations. In a dusty environment, a wider fin spacing can help prevent fouling, while a narrower spacing is more efficient in a clean room. The fin material, typically aluminum or copper, is chosen based on its thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. For specialized applications, like those involving corrosive liquids or high-purity air, materials like stainless steel may be necessary.

Retrofitting Older Systems: When to Clean, Repair or Replace Finned Tube Coils
Building owners with older HVAC systems often face a dilemma: when to clean, repair or replace finned tube coils. A professional assessment can help with this decision. If a coil is only moderately fouled, a deep cleaning might restore its performance. If it has a small leak, a repair might be a temporary fix. However, if a coil is old, corroded, and has multiple leaks, a full replacement is often the most cost-effective long-term solution. New, high-efficiency coils can often pay for themselves through reduced energy costs.
To effectively manage an HVAC system, you need data. Performance testing protocols are used to establish efficiency baselines for finned tube coils. These protocols involve measuring temperatures and pressures on both the air and fluid sides of the coil under controlled conditions. This data can be used to calculate a coil’s heat transfer rate and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications. Regular testing allows facility managers to monitor a coil’s performance over time and identify when maintenance is needed.
The Science of Coil Fouling: How Different Contaminants Impact Heat Transfer Efficiency
The science of coil fouling is surprisingly complex. Different contaminants impact heat transfer efficiency in unique ways. Dust and pollen form a porous layer that acts as an insulator and restricts airflow. Grease and oil, common in food processing facilities, create a sticky film that traps more dirt and is difficult to remove. Biological contaminants, like mold and algae, can create a slimy film that further degrades performance and can pose health risks. Understanding the nature of the fouling helps to determine the best cleaning method.
Finned tube coils are dual-surface heat exchangers, with a water or fluid side and an air side. Both require maintenance. Water-side maintenance involves managing water quality to prevent scale buildup and corrosion inside the tubes. This includes chemical treatments and regular flushing. Air-side maintenance focuses on keeping the fins clean. A comprehensive care plan addresses both sides to ensure the entire system remains in top condition, maximizing heat transfer efficiency and longevity.
Optimizing Fan and Pump Systems to Compensate for Aging Coil Performance
As coils age and become less efficient, the overall system must work harder. One strategy is to optimize the fan and pump systems. Optimizing fan and pump systems can help to compensate for aging coil performance. This might involve increasing fan speed to force more air over the coil or increasing the pump speed to push more liquid through it. However, this is a temporary solution that increases energy consumption and puts more stress on the equipment. It’s a stopgap measure until the coil can be properly cleaned or replaced.
When a facility manager is budgeting for maintenance, they often face a choice: spend money on a better filtration system or budget for frequent coil cleaning. A return on investment (ROI) analysis can help with this decision. Premium filtration systems have a higher upfront cost but reduce the need for cleaning, saving on labor and downtime. Frequent coil cleaning costs are a recurring expense that can add up quickly. The ROI analysis will often show that investing in better filtration is the more cost-effective choice over the long term, providing a cleaner system and lower energy bills.