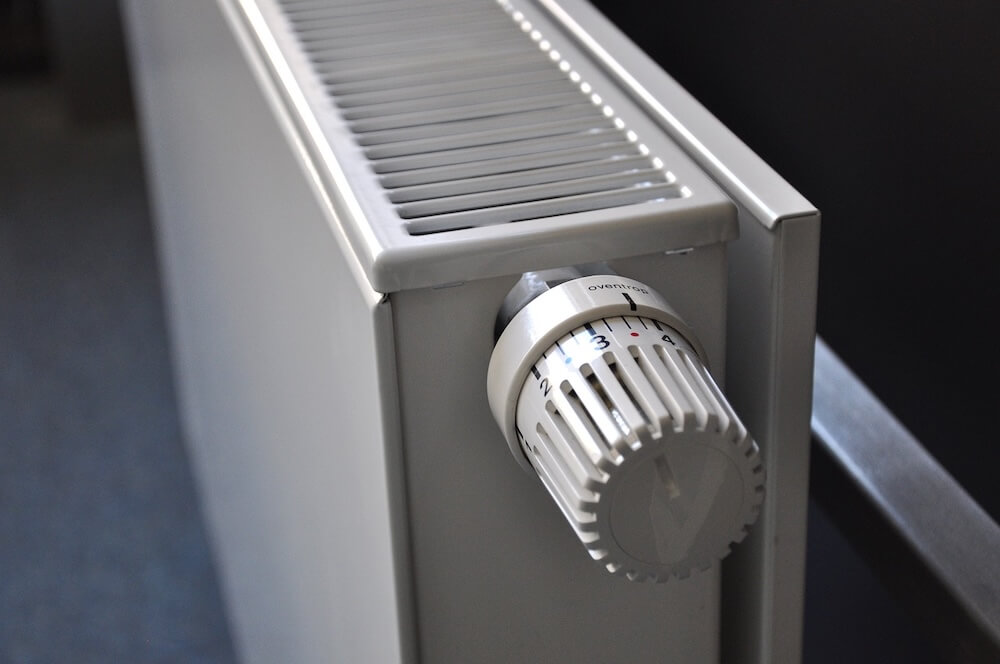
Radiators play a vital role in heating and cooling systems across various industries. One common design feature is the addition of fins, which are thin metal strips attached to the tubes or core of the radiator. But are radiators with fins truly more efficient than their finless counterparts? The answer lies in understanding how fins impact heat transfer, energy consumption, and system performance. In this article, we’ll explore the science behind finned radiators, their efficiency benefits, and the scenarios where they outperform alternative designs.
Radiators with fins are more efficient because the fins increase the surface area available for heat exchange, allowing for faster and more effective dissipation of heat into the surrounding air. This design reduces energy consumption and improves overall system performance.
How Do Fins Improve Radiator Efficiency?
To understand why fins make radiators more efficient, it’s essential to grasp the principles of heat transfer. In any radiator, the primary goal is to transfer heat from a fluid (such as water, coolant, or steam) inside the radiator to the surrounding air. This process occurs through conduction, convection, and, to a lesser extent, radiation.
Fins play a crucial role in the convection process by:
- Increasing Surface Area: Fins provide a larger surface for the heat to dissipate into the air. Without fins, the heat transfer is limited to the small surface area of the tubes or core.
- Enhancing Air Contact: The fins extend outward, ensuring that more air flows over the radiator and absorbs the heat.
- Improving Heat Distribution: By spreading the heat across a wider area, fins allow for more uniform temperature regulation.
Without fins, a radiator relies solely on the surface area of the tubes or panels, which limits its ability to cool or heat efficiently.
The Efficiency Metrics of Finned Radiators
Several factors demonstrate the improved efficiency of finned radiators:
- Faster Heat Dissipation: The increased surface area enables quicker heat transfer, reducing the time it takes to reach the desired temperature.
- Energy Savings: With more effective heat transfer, systems require less energy to maintain consistent temperatures, lowering operational costs.
- Compact Design: Finned radiators can achieve the same level of heat exchange as larger finless radiators, making them ideal for applications where space is a concern.
- Improved Thermal Conductivity: Fins made from materials like aluminum or copper maximize thermal conductivity, further boosting efficiency.
Where Are Finned Radiators Most Effective?
Finned radiators excel in scenarios where rapid heat dissipation and space efficiency are critical. Common applications include:
- Automotive Cooling Systems: Finned radiators in cars and trucks keep engine temperatures in check by efficiently dissipating heat from the coolant.
- HVAC Systems: In residential and commercial buildings, finned radiators distribute heat evenly, ensuring comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Industrial Heat Exchangers: Factories and power plants rely on finned radiators for cooling processes, such as steam condensation or air-cooled heat exchangers.
- Electronics Cooling: Finned designs are often used in computers, servers, and other electronics to prevent overheating.
Finned vs. Finless Radiators: A Comparison
While finned radiators are typically more efficient, there are cases where finless designs may be preferable. Let’s compare the two:
- Heat Transfer Efficiency:
- Finned: Superior due to the larger surface area.
- Finless: Limited by a smaller contact area with the air.
- Space Requirements:
- Finned: Compact and lightweight, suitable for tight spaces.
- Finless: Larger and bulkier to achieve similar heat transfer levels.
- Maintenance Needs:
- Finned: Require regular cleaning to prevent dust buildup on the fins, which can reduce airflow and efficiency.
- Finless: Easier to clean but may require more space for similar performance.
- Applications:
- Finned: Ideal for high-performance systems and confined spaces.
- Finless: Suitable for low-demand applications where space is not a constraint.
Potential Drawbacks of Finned Radiators
Despite their advantages, finned radiators have some limitations:
- Dust Accumulation: The gaps between fins can collect dust, reducing airflow and thermal efficiency. Regular cleaning is necessary to maintain performance.
- Higher Initial Costs: The materials and manufacturing processes for finned radiators are often more expensive than for simpler designs.
- Delicate Structure: Thin fins can be more prone to damage during handling or operation, especially in rugged environments.
Innovations in Finned Radiator Design
Advancements in materials and manufacturing have made finned radiators even more efficient. Some notable innovations include:
- Micro-Finned Radiators: These designs feature ultra-thin fins packed more densely, further increasing surface area and enhancing heat transfer in compact systems.
- Hybrid Materials: Combining high-conductivity materials like aluminum with corrosion-resistant coatings improves performance and longevity.
- Aerodynamic Fin Shapes: Optimized fin shapes reduce airflow resistance, improving cooling efficiency without increasing fan power.
- Self-Cleaning Coatings: New surface treatments prevent dust and debris buildup, minimizing maintenance needs.
How to Optimize the Efficiency of Finned Radiators
To get the best performance from a finned radiator, follow these tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the fins and check for damage to ensure consistent airflow and heat transfer.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the radiator is positioned to allow unrestricted airflow, and pair it with a high-quality fan if necessary.
- Choose the Right Material: Aluminum fins are lightweight and highly conductive, while copper offers superior thermal performance for demanding applications.
- Upgrade Insulation: In systems where heat retention is critical, ensure that piping and other components are well-insulated to prevent energy loss.
Final Thoughts
Radiators with fins are undeniably more efficient in most applications. By increasing the surface area for heat transfer and improving airflow dynamics, fins allow these radiators to achieve superior performance in compact, energy-saving designs. While they require more maintenance and may cost more upfront, their long-term benefits—such as reduced energy costs and improved system reliability—far outweigh these drawbacks.
If you’re designing or upgrading a heating or cooling system, choosing a radiator with fins is a smart investment. With their proven efficiency and versatility, finned radiators deliver outstanding performance in a wide range of industries and environments.
By understanding their advantages and addressing potential challenges, you can maximize the efficiency of your finned radiator and ensure years of reliable operation. Whether for industrial, automotive, or residential use, finned radiators remain the gold standard for effective heat exchange.