Low-finned tubes are essential components in heat exchangers, providing an efficient way to increase heat transfer without requiring large, bulky equipment. These tubes feature short, closely spaced fins along their exterior surface, which help to enhance surface area and optimize heat transfer in compact spaces. Low-finned tubes are widely used in applications like refrigeration, air conditioning, and chemical processing. In this guide, we’ll look at the different types of low-finned tubes and explore how each type benefits specific applications.
“Low-finned tubes come in various types based on fin shape, material, and manufacturing technique, each designed to enhance heat transfer efficiency in compact heat exchangers.” Understanding these types can help you choose the right low-finned tube for your cooling or heating needs.
1. Extruded Low-Finned Tubes
Extruded low-finned tubes are created by extruding fins directly from the tube’s material, forming a seamless connection between the fins and the tube itself. This process produces a durable, high-quality tube with enhanced heat transfer capabilities. Because the fins are part of the tube, there’s no risk of separation or gaps between the tube and fins, which improves thermal conductivity and durability.
Key Features of Extruded Low-Finned Tubes
- Seamless Fin Connection: The fins are an integral part of the tube, which maximizes heat transfer efficiency.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Made from corrosion-resistant materials like copper, aluminum, or stainless steel, these tubes are ideal for harsh environments.
- Durable and Long-Lasting: Extruded fins withstand wear and tear better than other types, making them suitable for continuous high-demand applications.
Extruded low-finned tubes are commonly used in high-pressure and corrosive environments, such as chemical processing plants, power generation, and industrial heat exchangers, where long-term durability and efficiency are critical.
2. Embedded Low-Finned Tubes
Embedded low-finned tubes are manufactured by inserting a separate fin material into grooves cut into the outer surface of the tube. The fins are embedded and then rolled or bonded into the grooves, creating a secure connection. This design allows the use of different materials for the tube and fins, giving engineers flexibility in choosing the right materials based on thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Key Features of Embedded Low-Finned Tubes
- Material Flexibility: Different materials can be used for the fins and the tube, allowing for greater customization based on the application’s requirements.
- Good Heat Transfer Performance: The embedded fins provide solid heat transfer efficiency, although slightly lower than extruded fins due to minor gaps at the interface.
- Moderate Durability: Embedded fins are well-attached but may not have the seamless integration of extruded fins, making them suitable for moderate heat exchange needs.
Embedded low-finned tubes are often used in applications where material customization is necessary, such as in environments with varying temperatures or chemical exposure. They are commonly found in HVAC systems, automotive cooling, and other mid-range heat exchangers.
3. L-Footed Low-Finned Tubes
L-footed low-finned tubes feature fins that are wrapped around the tube in an “L” shape, with the base of each fin forming a tight bond with the tube surface. This design provides a good connection and improves heat transfer efficiency while keeping manufacturing costs lower. The L-footed fin design is popular due to its balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Key Features of L-Footed Low-Finned Tubes
- Cost-Effective Solution: The L-footed design is more economical to manufacture than extruded or embedded finned tubes, making it suitable for budget-conscious applications.
- Secure Fin Attachment: The L-footed base ensures that the fins are firmly attached to the tube, allowing for effective heat transfer.
- Ideal for Moderate Pressure Applications: These tubes work well in moderate-pressure environments but may not have the durability of extruded fins in extreme conditions.
L-footed low-finned tubes are commonly used in HVAC systems, commercial refrigeration, and other applications that don’t require high-pressure tolerance. They provide a reliable, cost-effective option for boosting heat transfer efficiency in mid-range applications.
4. Serrated Low-Finned Tubes
Serrated low-finned tubes have fins with serrated or cut edges, creating multiple small surfaces for additional airflow and turbulence around the tube. This design increases the heat transfer rate by improving the airflow pattern and maximizing the fin’s interaction with the surrounding fluid or air. Serrated fins are particularly effective in forced-air cooling systems where high airflow is available.
Key Features of Serrated Low-Finned Tubes
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: The serrated fins break up airflow, increasing turbulence and enhancing the tube’s heat dissipation rate.
- Optimized for Forced-Air Systems: Serrated fins are most effective when used with high-speed airflow, making them ideal for applications like air-cooled heat exchangers and automotive radiators.
- Moderate Durability: While efficient, serrated fins can be more prone to damage from debris in the airflow, making them less durable in certain environments.
Serrated low-finned tubes are well-suited for applications that require high heat dissipation and airflow, such as in air-cooled condensers, automotive cooling, and HVAC systems. However, they may need regular cleaning to prevent debris buildup in the serrations.
5. Wrap-On Low-Finned Tubes
Wrap-on low-finned tubes are produced by wrapping a strip of fin material tightly around the tube and securing it. This type of fin tube offers the advantage of easy manufacturing and flexibility in fin spacing. The fins are not directly bonded to the tube surface, which can affect heat transfer slightly but is suitable for low-cost, moderate-performance applications.
Key Features of Wrap-On Low-Finned Tubes
- Easy Manufacturing: Wrap-on fins are straightforward and economical to produce, making them an accessible option for low-cost projects.
- Adjustable Fin Spacing: The spacing between fins can be adjusted, providing flexibility in airflow and heat transfer rates.
- Suitable for Low- to Medium-Pressure Systems: Wrap-on fins are best used in systems that don’t require high heat transfer efficiency or extreme durability.
Wrap-on low-finned tubes are ideal for lower-demand applications, such as in light commercial HVAC systems, low-cost heat exchangers, and basic cooling units. Their ease of manufacturing and flexibility make them popular for budget-conscious applications where extreme efficiency is not necessary.
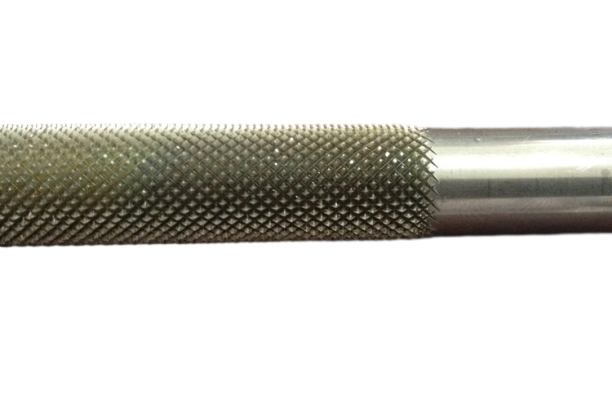
6. Knurled Low-Finned Tubes
Knurled low-finned tubes are made by adding a textured or knurled surface to the fins, which enhances heat transfer by increasing the turbulence of the surrounding fluid. This knurling improves the tube’s overall performance, particularly in liquid-to-liquid heat exchange applications where additional turbulence can increase efficiency.
Key Features of Knurled Low-Finned Tubes
- Improved Surface Turbulence: The knurled surface disrupts the fluid flow, increasing heat transfer rates by enhancing turbulence around the tube.
- Effective in Liquid Heat Exchangers: Knurled fins work especially well in liquid-based systems, where enhanced turbulence boosts heat transfer.
- Enhanced Efficiency: This design improves heat transfer without significantly increasing the tube’s size, making it a good choice for compact systems.
Knurled low-finned tubes are commonly used in liquid-to-liquid heat exchangers, chemical processing, and power generation, where maximizing efficiency in compact spaces is crucial.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right type of low-finned tube depends on the specific heat transfer requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints of the application. Extruded low-finned tubes offer maximum durability and heat transfer efficiency, while embedded and L-footed tubes provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness. For high airflow and enhanced turbulence, serrated and knurled fin tubes are excellent options, while wrap-on tubes offer a low-cost solution for moderate demands.
Summary: Low-finned tubes come in several types—extruded, embedded, L-footed, serrated, wrap-on, and knurled—each suited for different heat transfer applications. Selecting the best type depends on factors like efficiency, durability, and cost.
By understanding the unique properties of each type of low-finned tube, you can select the one that best meets the needs of your cooling or heating system, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.