The condenser is a crucial part of a refrigerator’s cooling system, responsible for releasing heat and keeping the appliance running efficiently. Understanding how the condenser works can help you better appreciate how your refrigerator keeps food fresh, as well as what to do if it starts to malfunction. In this guide, we’ll walk through the role of the condenser in a refrigerator, how it operates, and why it’s essential for maintaining optimal cooling performance.
“In a refrigerator, the condenser releases heat absorbed from inside the fridge to the surrounding air, allowing the refrigerant to cool and return to the evaporator to absorb more heat.” This cycle is key to the refrigeration process, helping maintain a cold environment inside the fridge.
What is a Condenser in a Refrigerator?
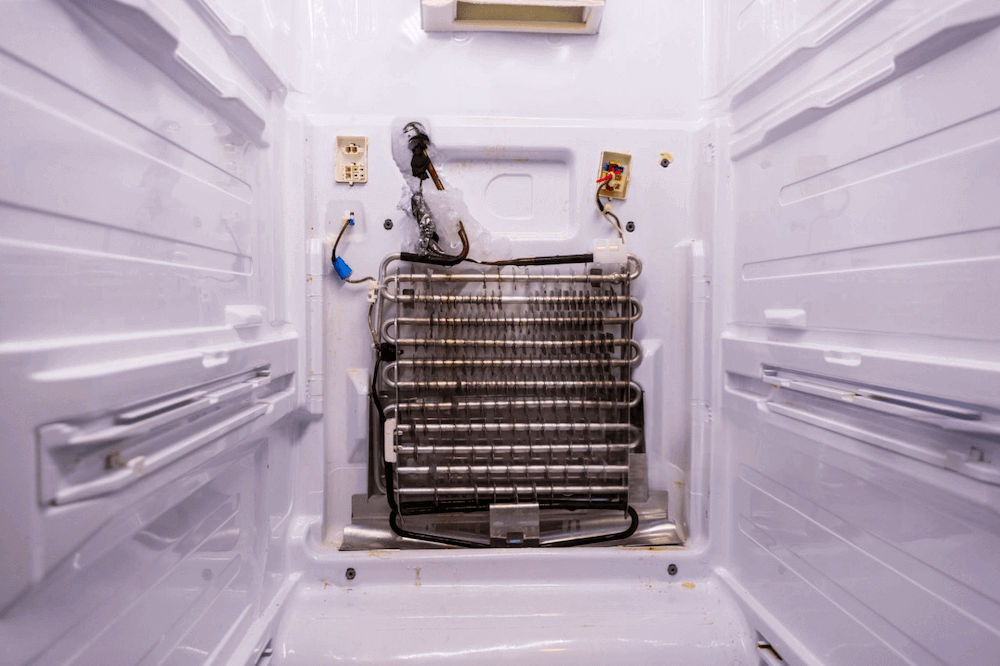
The condenser is one of the main components of a refrigerator’s cooling system, along with the compressor, evaporator, and expansion valve. Located either at the back or bottom of the fridge, the condenser is a series of coiled pipes or tubes, often made from copper or aluminum for efficient heat transfer. Its primary role is to release the heat absorbed from inside the refrigerator to the external environment.
The condenser works in tandem with the other components, allowing the refrigerant (a cooling fluid) to cycle through a process of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation. This continuous cycle enables the refrigerator to maintain a cold temperature by removing heat from inside and releasing it outside.
How the Condenser Works in the Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle is a closed loop, with the condenser playing a key role in releasing heat. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the condenser functions within this cycle:
1. Compression of Refrigerant
The process begins with the compressor, which compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas is then pushed into the condenser coils.
- Compressor Function: The compressor squeezes the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature, effectively “pushing” it through the refrigeration system.
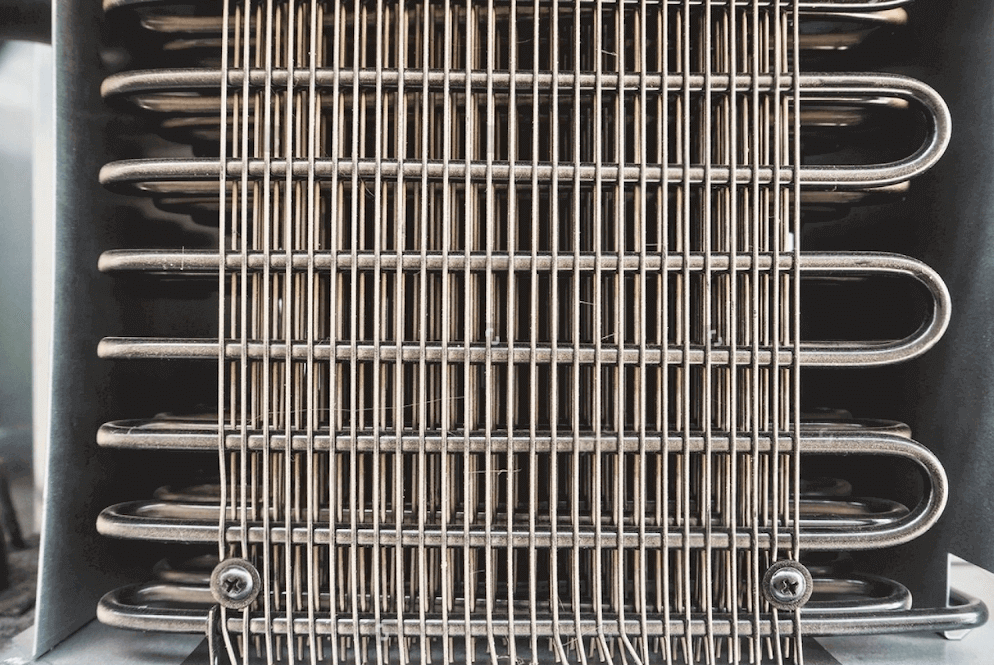

2. Condensation and Heat Release in the Condenser
Once the high-pressure refrigerant enters the condenser coils, it starts to cool down as it passes through. The condenser coils are exposed to the outside air, often with a fan that blows air across the coils to enhance cooling. As the refrigerant cools, it changes from a high-pressure gas into a high-pressure liquid, releasing the absorbed heat to the surrounding air in the process.
- Heat Dissipation: The heat absorbed from inside the refrigerator is released into the environment as the refrigerant condenses. This step is critical in keeping the refrigerator’s interior cool.
- Phase Change: The refrigerant changes from gas to liquid as it cools, which is essential for restarting the cycle in the evaporator.
3. Flow to the Expansion Valve
After leaving the condenser, the now-liquid refrigerant flows through an expansion valve or capillary tube. This valve reduces the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature, preparing it to enter the evaporator coil inside the refrigerator.
- Pressure Reduction: By reducing the pressure, the expansion valve allows the refrigerant to cool rapidly before it enters the evaporator.
- Preparation for Cooling: The cooled, low-pressure liquid refrigerant is now ready to absorb heat in the evaporator coil.
4. Absorbing Heat in the Evaporator
In the evaporator coil, the low-pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from inside the refrigerator, cooling the air. This heat absorption causes the refrigerant to evaporate back into a gas, which then returns to the compressor, and the cycle starts again.
Why the Condenser is Essential for Refrigerator Performance
The condenser’s role in releasing heat is essential for the refrigerator to maintain a cold environment inside. Here’s why the condenser is critical to the refrigerator’s performance:
1. Maintains a Stable Temperature
By continuously releasing heat to the external environment, the condenser helps maintain a stable temperature within the refrigerator. Without the condenser, heat absorbed from the fridge’s interior would remain in the refrigerant, making it impossible to cool the refrigerator effectively.
2. Enables Efficient Refrigerant Flow
The condenser enables the refrigerant to change from gas to liquid, an essential step in the refrigeration cycle. This phase change allows the refrigerant to absorb heat efficiently when it returns to the evaporator, ensuring the cycle can continue without interruption.
3. Reduces Energy Consumption
An efficient condenser reduces the load on the compressor by releasing heat quickly, which minimizes energy consumption. When the condenser works well, the compressor doesn’t need to work as hard to maintain a cool environment, resulting in lower energy usage and extending the compressor’s lifespan.
Types of Condensers Used in Refrigerators
There are two primary types of condensers commonly found in refrigerators:
1. Air-Cooled Condensers
Air-cooled condensers are the most common type found in household refrigerators. They rely on air circulation to cool the refrigerant, typically with the help of a fan. These condensers are usually located at the back or bottom of the refrigerator.
- Advantages: Air-cooled condensers are effective, affordable, and easy to maintain.
- Limitations: They can be affected by ambient room temperature; in very hot environments, their efficiency may drop.
2. Water-Cooled Condensers
Water-cooled condensers are less common in household refrigerators but are used in some commercial models. Instead of air, water circulates around the condenser coils to cool the refrigerant. Water-cooled condensers are generally more efficient than air-cooled ones, especially in hot environments.
- Advantages: Water-cooled condensers can achieve greater efficiency, particularly in areas with high ambient temperatures.
- Limitations: They require a steady supply of water and more complex maintenance, which is why they are less common in residential models.
Signs of Condenser Problems in a Refrigerator
A malfunctioning condenser can lead to reduced cooling efficiency and increased energy usage. Here are some common signs that the condenser may not be working correctly:
1. Refrigerator Not Cooling Properly
If the refrigerator isn’t maintaining a cold temperature, it could indicate a problem with the condenser. When the condenser can’t release heat effectively, the refrigerator will struggle to cool the interior.
2. Increased Energy Bills
An inefficient or dirty condenser can cause the refrigerator to consume more power. The compressor has to work harder to compensate for the condenser’s reduced efficiency, leading to higher electricity usage.
3. Unusual Noises
If you hear unusual noises from the back or bottom of the refrigerator, it could indicate that the condenser fan or coils are malfunctioning. Loose or damaged components may create rattling or buzzing sounds, signaling that maintenance is needed.
4. Condenser Coils Feel Hot
It’s normal for condenser coils to feel warm, but if they are excessively hot, it may be a sign that the condenser isn’t releasing heat effectively. This can occur due to a dirty or blocked condenser, which may require cleaning.
Tips for Maintaining a Refrigerator Condenser
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the condenser operates efficiently. Here are some tips for keeping your refrigerator’s condenser in good condition:
- Clean the Coils Regularly: Dust and dirt can accumulate on the coils, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Clean the condenser coils every 6 to 12 months to keep them free from debris.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Make sure there is enough space around the refrigerator for airflow. Blocked vents or insufficient space can reduce the condenser’s cooling efficiency.
- Inspect the Fan: If your refrigerator has a condenser fan, check it regularly to ensure it’s working properly. A malfunctioning fan can hinder the condenser’s ability to release heat.
- Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect the area around the condenser for refrigerant leaks, which can affect cooling performance. Leaks should be repaired by a professional.
The condenser is an essential component in a refrigerator, releasing heat from inside the appliance and enabling the cooling cycle to continue efficiently. By understanding how the condenser works and maintaining it properly, you can ensure your refrigerator operates at peak performance, keeping your food fresh and your energy bills low.
Summary: The condenser in a refrigerator releases heat absorbed from inside the fridge, cooling the refrigerant and allowing it to repeat the cooling cycle. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the coils, is essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Proper care and awareness of the condenser’s function can help you enjoy reliable cooling in your refrigerator for years to come.