Fin tube radiation is a cornerstone technology in modern heating systems, offering efficient, reliable, and consistent warmth in residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. Despite its widespread use, many people don’t fully understand how this technology works or how to optimize its performance. In this article, we’ll break down the mechanics, benefits, and considerations of fin tube radiation, helping you make informed decisions about installation, maintenance, or upgrades.
Fin tube radiation works by using finned metal tubes to maximize heat transfer, allowing hot water or steam to efficiently warm a space through a combination of convection and radiation. This system is energy-efficient, compact, and ideal for applications where steady, uniform heat is required.
What Is Fin Tube Radiation?
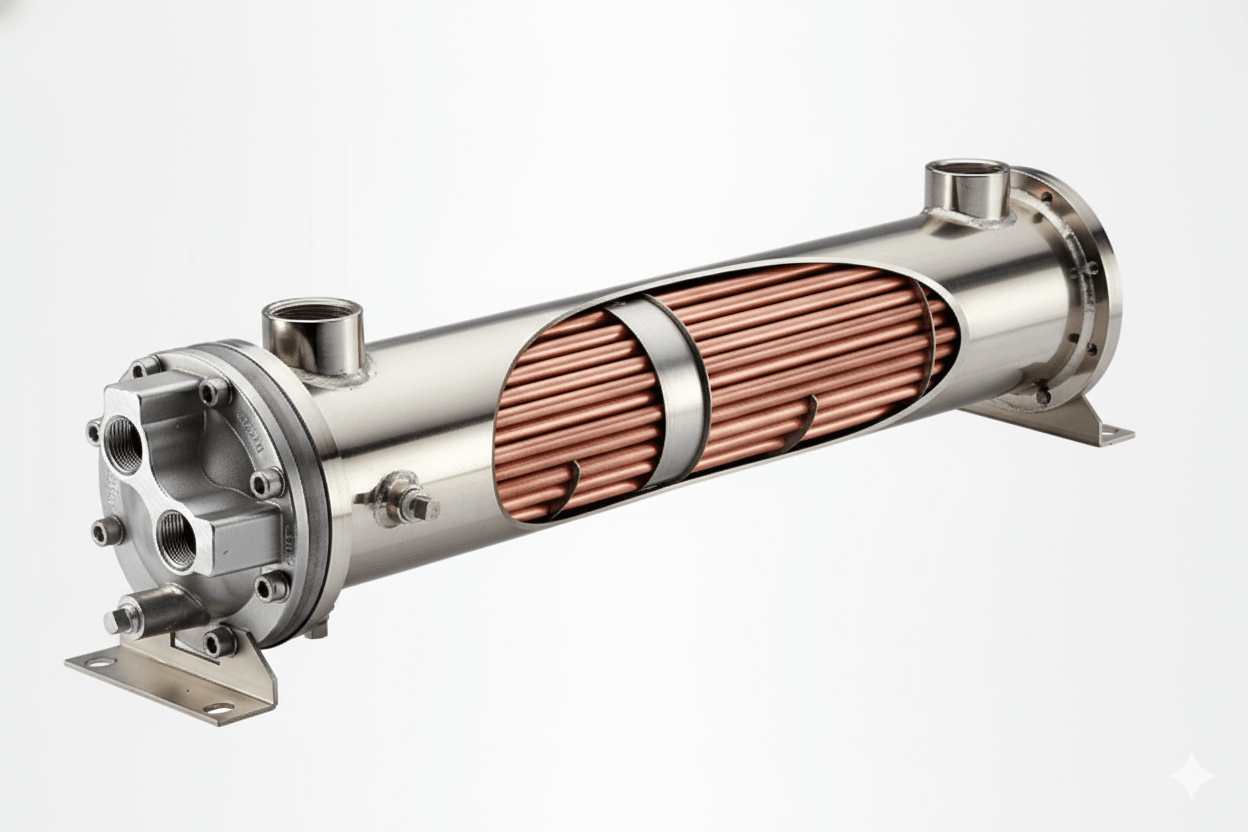
Fin tube radiation is a heating system that uses a series of metal tubes equipped with thin, fin-like structures to distribute heat. These tubes are typically mounted along walls or floors and connected to a boiler system. The boiler circulates hot water or steam through the tubes, which transfer heat to the surrounding air via convection and radiate warmth into the room. The fins are the key component—they significantly increase the surface area of the tubes, improving heat transfer efficiency.
How Does Fin Tube Radiation Work?
The operation of fin tube radiation involves three primary steps:
- Heat Generation: A boiler heats water or produces steam, which is then circulated through the fin tubes.
- Heat Transfer: As the hot water or steam flows through the tubes, the metal surface absorbs the heat. The attached fins help disperse this heat by increasing the surface area exposed to the surrounding air.
- Air Circulation: Warm air rises naturally, creating a convection current that circulates warmth throughout the room. At the same time, some heat radiates directly from the fins and tubes, providing steady, comfortable heating.
Key Components of Fin Tube Radiation
- Base Tube: Typically made of materials like copper or steel, the tube carries the heated fluid.
- Fins: Thin metal strips, usually aluminum or steel, are attached to the tube. These fins dramatically increase the surface area for heat transfer.
- Enclosure: A protective cover or housing encases the fin tube system. This enclosure often includes slats or vents to direct airflow and improve heat distribution.
- Control Valves: These regulate the flow of hot water or steam, allowing for temperature adjustments and energy efficiency.
Benefits of Fin Tube Radiation
- High Efficiency: The fins enable rapid heat transfer, reducing the time and energy required to warm a space.
- Compact Design: Fin tube systems are sleek and unobtrusive, making them ideal for areas where space is limited.
- Quiet Operation: Unlike forced-air systems, fin tube radiation operates silently, with no fans or motors involved.
- Customizable Output: By adjusting the fin density or material, engineers can tailor the system to specific heating requirements.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, these systems are easy to maintain and have a long lifespan.
Applications of Fin Tube Radiation
Fin tube radiation is used in a variety of settings, including:
- Residential Homes: For consistent and silent heating in living spaces, bedrooms, and basements.
- Commercial Buildings: Offices, schools, and retail spaces benefit from its energy efficiency and compact design.
- Industrial Facilities: It provides reliable heating in warehouses, workshops, and production areas.
- Greenhouses: The uniform heat distribution is ideal for maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Challenges and Solutions in Fin Tube Radiation
- Dust Accumulation: Dust can accumulate on the fins, reducing efficiency. Regular cleaning is essential to maintain performance.
- Uneven Heat Distribution: Poor installation or improper balancing can lead to cold spots. This can be solved by ensuring proper placement and adjusting flow rates with control valves.
- Corrosion: Over time, water and air exposure can corrode the tubes. Using corrosion-resistant materials like copper or applying protective coatings can mitigate this issue.
How to Optimize Fin Tube Radiation Performance
To maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your fin tube radiation system, consider the following tips:
- Choose the Right Material: Copper is ideal for its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, while steel is a more budget-friendly option.
- Proper Installation: Work with experienced professionals to ensure the system is correctly balanced and placed for optimal heat distribution.
- Routine Maintenance: Clean the fins and inspect the system annually to prevent dust buildup and detect potential issues early.
- Upgrade Insulation: Improving the insulation around your home or building will enhance the performance of your heating system and reduce energy costs.
Unique Insights: Why Fin Tube Radiation Stands Out
One of the most overlooked advantages of fin tube radiation is its flexibility in hybrid heating systems. In modern setups, fin tube systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources like solar thermal panels or geothermal systems. This reduces reliance on traditional boilers, lowering carbon footprints and operating costs.
Additionally, advanced designs, such as low-temperature fin tubes, are becoming more popular. These systems work efficiently at lower water temperatures, making them compatible with condensing boilers or heat pumps for even greater energy savings.
Final Thoughts
Fin tube radiation is a proven, efficient, and versatile heating solution suitable for a wide range of applications. Its compact design, energy efficiency, and low maintenance requirements make it an attractive choice for residential and commercial users alike.
If you’re considering a new heating system or looking to upgrade your current setup, fin tube radiation offers a cost-effective and reliable option. By understanding how it works and implementing best practices for maintenance and optimization, you can enjoy consistent warmth and significant energy savings for years to come.
Whether you’re designing a new building or retrofitting an old one, fin tube radiation provides a balance of performance and practicality that few systems can match.