In cooling and heat exchange applications, two popular types of heat exchangers are the plate fin cooler and the shell-and-tube cooler. Each type has a unique design, set of benefits, and ideal applications that make it suited for specific industrial and commercial needs. This guide compares the two, explaining how they differ in construction, efficiency, and use cases to help you decide which is best for your system.
“A plate fin cooler is compact and highly efficient, ideal for applications with limited space, while a shell-and-tube cooler offers durability and is preferred for heavy-duty industrial use.” Understanding the key differences can help optimize heat transfer based on your cooling needs.
What is a Plate Fin Cooler?
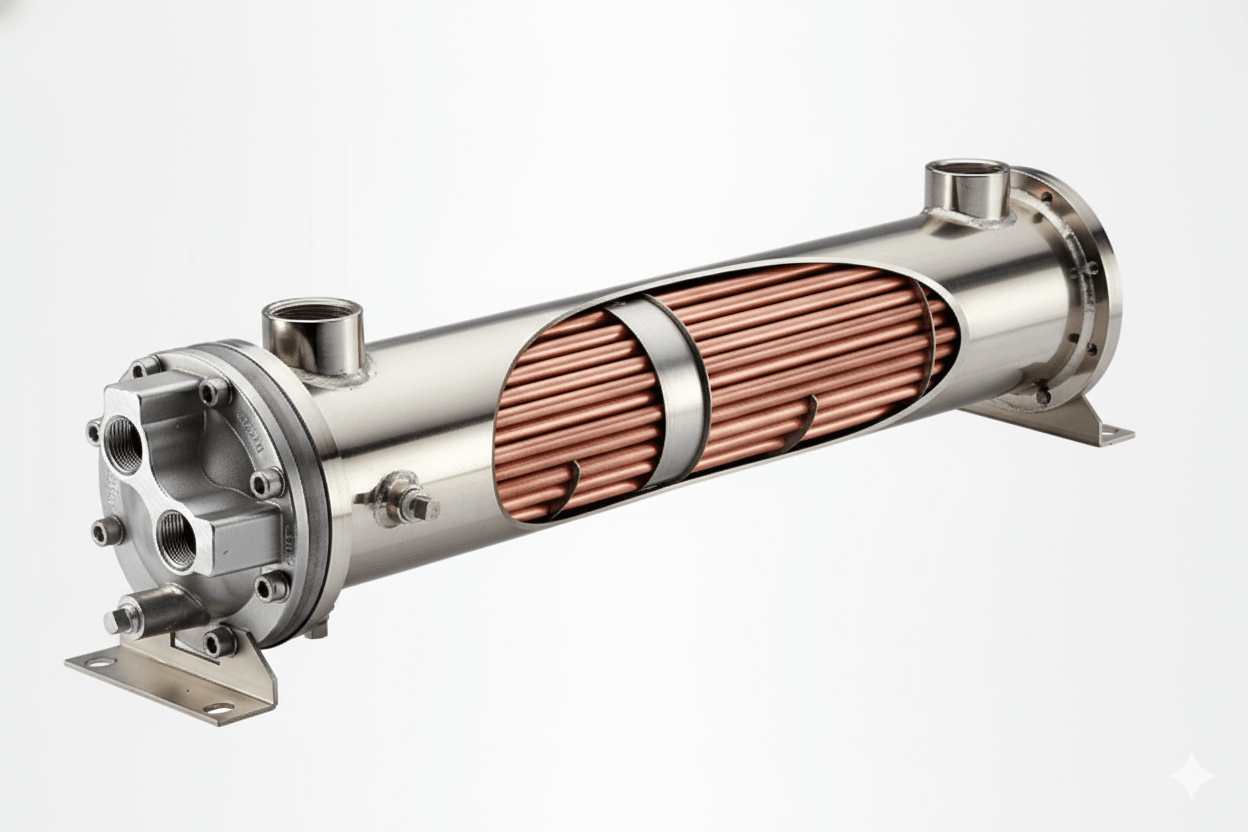
A plate fin cooler is a type of heat exchanger that uses thin, flat plates with attached fins to maximize surface area for heat transfer. In this design, the plates and fins are stacked in layers, and fluids flow through alternate layers, allowing heat to transfer from one fluid to the other across the plates. This arrangement increases heat exchange efficiency and enables the unit to achieve high thermal performance in a compact structure.
Key Features of Plate Fin Coolers
- High Surface Area: The design maximizes surface area, which enhances heat transfer and makes the cooler highly efficient.
- Compact and Lightweight: Due to the stacked plate structure, plate fin coolers are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for applications with limited space.
- Efficient Heat Transfer: Plate fin coolers can achieve high heat transfer rates, making them effective even in low-temperature or low-pressure applications.
What is a Shell-and-Tube Cooler?
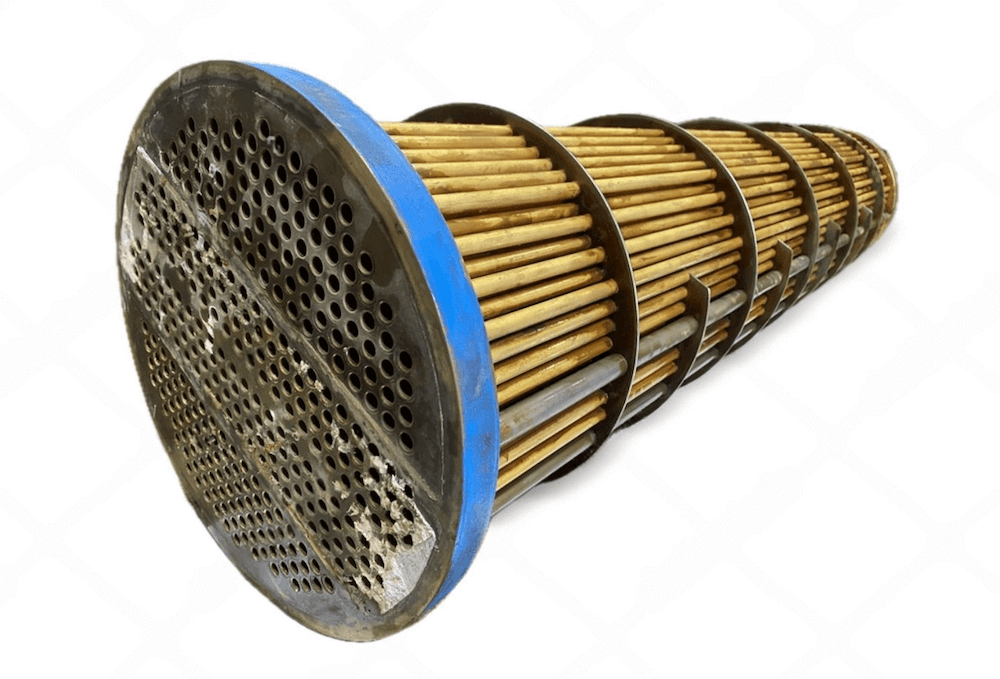
A shell-and-tube cooler, also called a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, consists of a series of tubes (the “tube bundle”) placed inside a cylindrical shell. In this design, one fluid flows inside the tubes, while the other flows around the tubes within the shell. Heat transfer occurs as the two fluids pass by each other, with one fluid cooling the other through the tube walls. Shell-and-tube coolers are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications, where durability and high-pressure tolerance are essential.
Key Features of Shell-and-Tube Coolers
- Durable Design: The cylindrical shell and tube bundle are built to withstand high pressures, making them durable for heavy-duty applications.
- Ideal for High Temperatures and Pressures: The design can handle extreme temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for industrial and chemical processing.
- Flexible Configuration Options: Shell-and-tube coolers come in various configurations, including U-tube, straight-tube, and floating head designs, to suit different applications.
Comparing Plate Fin Coolers and Shell-and-Tube Coolers
While both types serve similar purposes, plate fin coolers and shell-and-tube coolers differ in significant ways. Here’s a closer look at how they stack up in terms of design, efficiency, durability, and use cases.
1. Design and Construction
The core structural difference between plate fin coolers and shell-and-tube coolers lies in their heat exchange design.
- Plate Fin Cooler: This cooler features flat plates stacked with fins in between, creating a high surface area for heat transfer. The compact design allows more heat exchange in a smaller space, making it ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Shell-and-Tube Cooler: This type consists of a series of tubes within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows around them in the shell. The shell-and-tube design is bulkier but offers greater durability and can handle high pressures and temperatures, which makes it a robust option for industrial settings.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency
Heat transfer efficiency is crucial for any cooling system. Here’s how each type compares:
- Plate Fin Cooler: With its high surface area from the fins and plates, the plate fin cooler provides excellent heat transfer efficiency. The increased surface area allows for more rapid heat exchange, making it highly efficient in low-pressure or low-temperature applications.
- Shell-and-Tube Cooler: Shell-and-tube coolers are also efficient but are typically less efficient in terms of heat transfer compared to plate fin coolers. However, their design allows them to handle more substantial flow rates and higher temperatures, making them suitable for systems that require continuous high-capacity cooling.
3. Space Requirements
Space availability can be a limiting factor, especially in smaller installations or mobile systems.
- Plate Fin Cooler: Known for its compact and lightweight design, the plate fin cooler requires less space. This makes it ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and other sectors where space constraints are common.
- Shell-and-Tube Cooler: Due to its cylindrical design and tube bundle, shell-and-tube coolers are bulkier and heavier. They require more space and are typically installed in areas where space is not a major constraint, such as large industrial plants or processing facilities.
4. Durability and Maintenance
Durability and ease of maintenance are important factors for long-term system performance.
- Plate Fin Cooler: While efficient, plate fin coolers can be more susceptible to fouling and clogging between the fins. They may require regular cleaning, especially in applications where the fluids have impurities. However, they are generally easy to replace and have a lower cost.
- Shell-and-Tube Cooler: Shell-and-tube coolers are highly durable and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial use. They are also easier to maintain and clean, as the tube bundle can often be removed for internal cleaning. This design feature is beneficial for applications in oil and gas, petrochemical, and chemical processing where durability is critical.
Applications of Plate Fin Coolers vs. Shell-and-Tube Coolers
Each cooler type has specific applications where it excels. Here’s a look at where each cooler is best suited:
1. Plate Fin Cooler Applications
- Aerospace: Due to their compact size and high efficiency, plate fin coolers are ideal for aerospace applications where weight and space are limited.
- Automotive and Hydraulic Systems: In automotive systems, plate fin coolers are used for oil cooling, transmission cooling, and hydraulic systems due to their high efficiency in a small form factor.
- HVAC Systems: Plate fin coolers are commonly used in HVAC systems where compact cooling units are required for efficient air conditioning and refrigeration.
2. Shell-and-Tube Cooler Applications
- Industrial Processing: The durability and pressure resistance of shell-and-tube coolers make them a preferred choice in heavy industrial applications, such as oil refining and chemical processing.
- Power Generation: These coolers are frequently used in power plants to cool fluids under high-pressure conditions.
- Petrochemical Applications: In the petrochemical industry, shell-and-tube coolers are used due to their ability to handle corrosive fluids, high temperatures, and extreme pressures.
Choosing Between Plate Fin and Shell-and-Tube Coolers
When deciding between a plate fin cooler and a shell-and-tube cooler, consider the specific needs of your system:
- For Space-Sensitive Applications: Plate fin coolers are ideal for systems where space is limited and high efficiency is required. They are best suited for applications like automotive, aerospace, and compact HVAC systems.
- For High-Pressure and Heavy-Duty Applications: If your application involves high pressures, extreme temperatures, or continuous operation, a shell-and-tube cooler is typically the better choice. It provides the durability and robustness needed for industrial and petrochemical processes.
Final Thoughts
Both plate fin coolers and shell-and-tube coolers have unique features that make them suited for different types of cooling applications. By understanding their strengths and limitations, you can select the type of cooler that best fits your system’s requirements, whether for compact efficiency or high-capacity durability.
Summary: Plate fin coolers are compact, efficient, and ideal for space-limited applications, while shell-and-tube coolers are durable, capable of handling high pressures, and well-suited for heavy-duty industrial environments. Knowing these differences can help you make the best choice for your cooling system needs.
Selecting the right type of cooler ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity for your equipment and can ultimately lead to cost savings and improved reliability in your cooling operations.