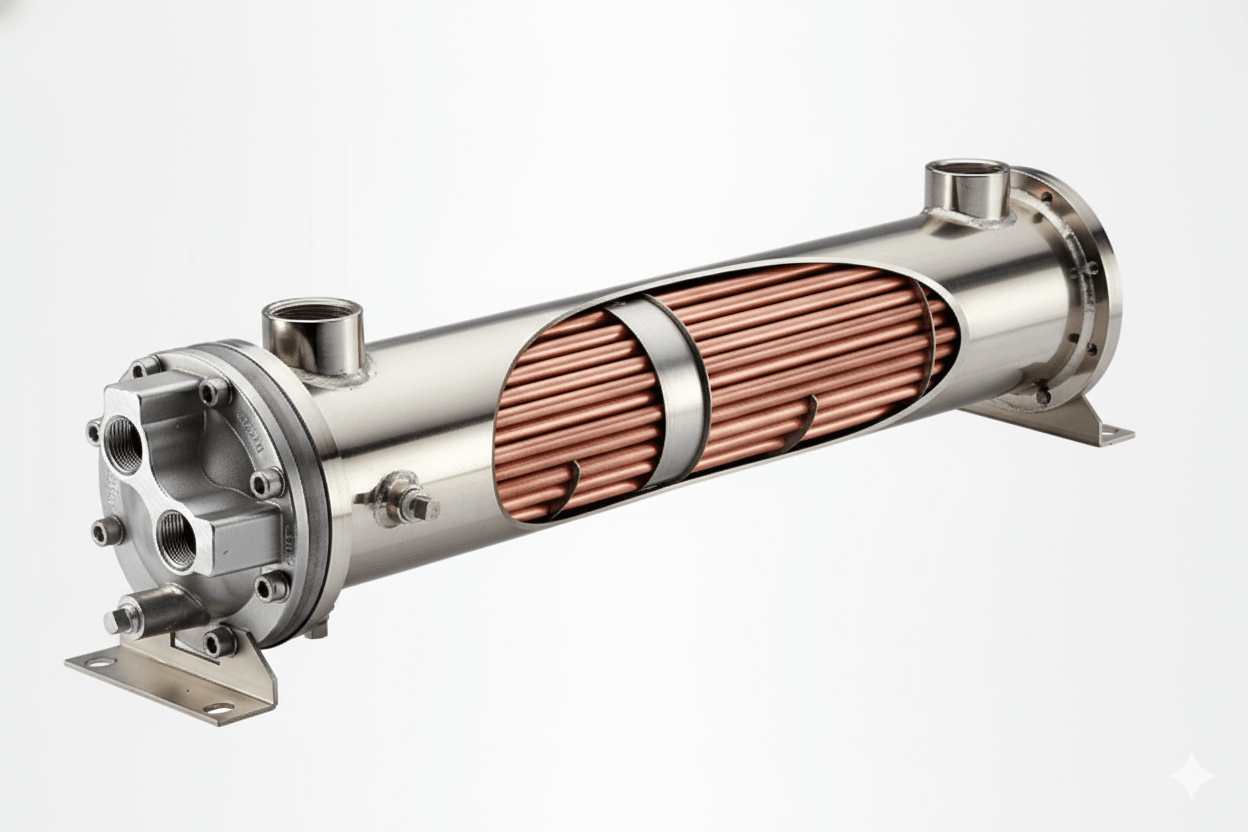
Finned tube heat exchangers are essential in industries that require efficient heat transfer, such as HVAC, power generation, and refrigeration. These heat exchangers come in various types, each designed to optimize heat transfer for specific applications. Understanding the different types of finned tube heat exchangers and knowing when to use each design can help improve system efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and enhance durability. In this guide, we’ll explore the main types of finned tube heat exchangers, including their applications and benefits.
“Finned tube heat exchangers vary in design to meet specific heat transfer needs. Each type offers unique benefits based on efficiency, airflow, and space constraints, making them ideal for a range of heating and cooling applications.” Knowing the types and when to use them can guide you to the best solution for your application.
1. Plain Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Plain finned tube heat exchangers feature simple, flat fins attached around the tube to increase the surface area for heat transfer. These fins are generally made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, to enhance thermal conductivity. Plain fins are widely used in applications that don’t require extreme heat transfer rates but still need efficient temperature control.
When to Use Plain Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- For Moderate Heating or Cooling Needs: Plain finned tubes are ideal for applications where moderate heat transfer is sufficient, such as in residential HVAC systems or air-cooled heat exchangers.
- Where Simplicity and Durability Matter: With their straightforward design, plain finned tubes are easy to maintain and durable, making them a good choice for applications that prioritize long-lasting performance.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Since they’re simpler in design, plain finned tubes are often more affordable than other types, which is beneficial for projects with limited budgets.
2. Serrated Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Serrated finned tube heat exchangers have fins with serrated or cut edges, which create small gaps along the edges of the fins. These gaps improve airflow turbulence, allowing heat to be transferred more effectively from the tube to the surrounding air. Serrated fins are especially useful in applications requiring high heat transfer rates and efficient cooling in a compact design.
When to Use Serrated Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- For High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The serrated edges enhance heat transfer by creating more turbulence in the airflow, which makes these heat exchangers suitable for high-efficiency systems like industrial refrigeration or automotive radiators.
- In Forced-Air Cooling Systems: Serrated finned tubes are often used in forced-air systems where fans or blowers push air across the fins. The airflow turbulence created by the serrations improves the heat exchanger’s cooling performance.
- Space-Constrained Environments: Due to their increased efficiency, serrated finned tubes can be used in compact designs without sacrificing performance, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
3. Helical Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Helical finned tube heat exchangers feature fins that are wrapped in a spiral pattern around the tube. This helical design increases surface area and enhances the turbulence of the fluid, which improves heat transfer efficiency. Helical fins are popular in applications where efficient heat exchange is necessary, especially when using liquids or gases with moderate to high viscosity.
When to Use Helical Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- For Applications with Viscous Fluids: Helical finned tubes are well-suited for systems where the fluid has a higher viscosity, such as oil coolers or industrial process heat exchangers. The helical design improves fluid movement along the fins, enhancing heat transfer.
- In High-Efficiency Heating Systems: Due to their design, helical fins maximize contact with the fluid, making them efficient for high-temperature applications, like boilers or gas heaters.
- Where Consistent Temperature Control is Required: The uniform wrap of helical fins promotes stable heat transfer, which is beneficial in applications where consistent temperature control is essential.
4. L-Footed Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
L-footed finned tube heat exchangers use L-shaped fins that wrap around the tube, with one side of the “L” bonded to the tube’s surface. This L-footed design creates a firm attachment between the tube and fin, providing good durability and heat transfer. They are often used in systems where moderate performance and budget considerations are important.
When to Use L-Footed Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- For Moderate Temperature Applications: L-footed finned tubes are ideal for heating or cooling systems where the temperature demands are moderate, such as HVAC systems or low-cost heating units.
- Where Durability and Affordability are Important: The L-footed design is economical to produce and durable, making it a practical choice for applications that require reliable, cost-effective heat transfer.
- In Systems with Mild Environmental Exposure: These finned tubes are suitable for indoor or lightly exposed environments, as they offer durability without the additional corrosion resistance of other types.
5. Extruded Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Extruded finned tube heat exchangers are manufactured by extruding the fins directly from the tube’s material, creating a seamless, one-piece structure. This design maximizes heat transfer efficiency and enhances durability, making them ideal for high-performance systems. Extruded finned tubes are often made from aluminum or copper and are highly resistant to corrosion.
When to Use Extruded Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- For High-Performance Heat Transfer: Extruded fins provide excellent thermal contact with the tube, resulting in high heat transfer efficiency. They are ideal for applications that require robust performance, such as power plants, refineries, and heavy industrial processes.
- In Corrosive or Harsh Environments: Since extruded fins have no seams or welds, they are highly resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or salt.
- Long-Term, High-Demand Applications: Extruded finned tubes are durable and reliable, making them the best choice for systems that operate continuously under high demand.
6. Embedded Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Embedded finned tube heat exchangers are made by inserting fins into grooves on the tube’s surface and then rolling or bonding them securely into place. This method allows for flexibility in materials, as the fins and tubes can be made from different metals. Embedded finned tubes are suitable for applications where moderate heat transfer is needed and where specific materials are required for thermal or corrosion resistance.
When to Use Embedded Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- In Custom Material Applications: The design flexibility of embedded fins allows engineers to select different materials for the tube and fins, making these heat exchangers suitable for applications where material compatibility is crucial, such as chemical processing.
- For Moderate Heat Transfer Needs: Embedded finned tubes provide effective heat transfer without the extreme efficiency of extruded fins, making them ideal for mid-range heating and cooling applications.
- Where Cost and Customization are Important: The embedded design is typically more affordable than extruded fins and allows for customization, making it a practical choice for projects with specific material requirements or budget limitations.
Selecting the Right Finned Tube Heat Exchanger Design
Choosing the right type of finned tube heat exchanger depends on the specific needs of your application. Here are some factors to consider:
- Heat Transfer Efficiency: For applications that require maximum heat transfer, such as industrial or power plant systems, extruded or serrated finned tubes are the best choice.
- Environmental Conditions: In harsh or corrosive environments, extruded finned tubes offer high durability. For indoor or lightly exposed applications, more economical designs like L-footed or plain fins may suffice.
- Space Constraints: Serrated or helical finned tubes are suitable for compact systems, while plain finned tubes are effective when space is not as limited.
- Budget Considerations: For cost-sensitive projects, L-footed or plain finned tubes are budget-friendly without sacrificing performance in moderate conditions.
By understanding the different types of finned tube heat exchangers, you can select the best design for your specific requirements, balancing efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Final Thoughts
Each type of finned tube heat exchanger has unique advantages, making it suitable for different heating and cooling applications. From the cost-effective plain finned tube to the highly efficient extruded finned tube, choosing the right design depends on factors such as heat transfer needs, environmental exposure, space constraints, and budget. Selecting the appropriate finned tube heat exchanger type can enhance performance, reduce energy costs, and ensure long-term reliability in your heating or cooling system.
With a clear understanding of each type and its ideal application, you can confidently choose the best finned tube heat exchanger to meet your specific thermal management needs.