Low fin tubes are essential components in heat exchange and cooling applications across various industries. Known for their efficiency in transferring heat, low fin tubes are especially useful in compact heat exchangers, refrigeration, and HVAC systems. This guide will explain what low fin tubes are, their benefits, applications, and key factors purchasers should consider before buying.
“A low fin tube is a type of heat exchanger tube with shallow, evenly spaced fins along its outer surface, designed to increase surface area and improve heat transfer efficiency in compact systems.” Understanding how low fin tubes work and their ideal applications can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What is a Low Fin Tube?
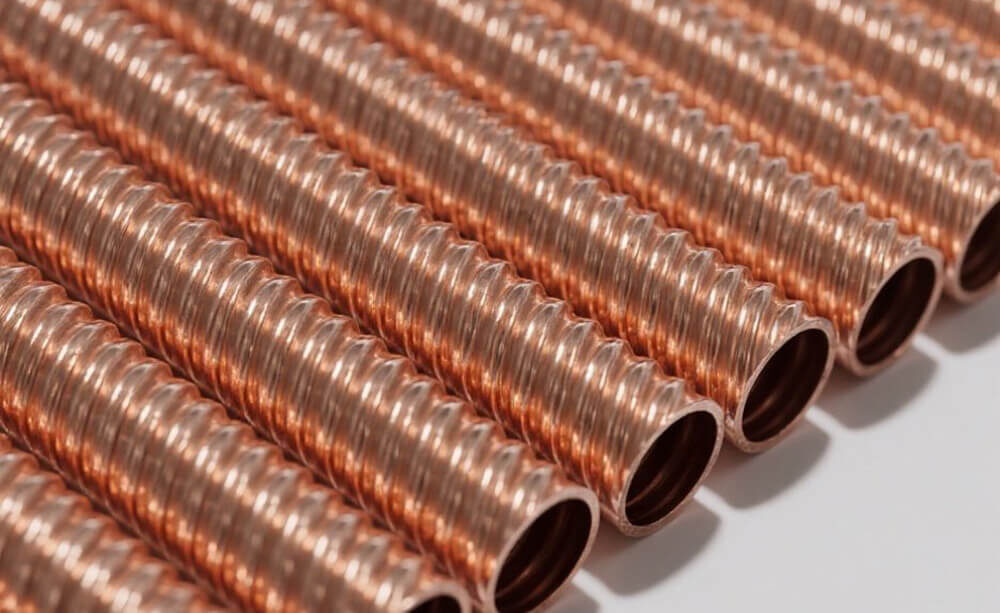
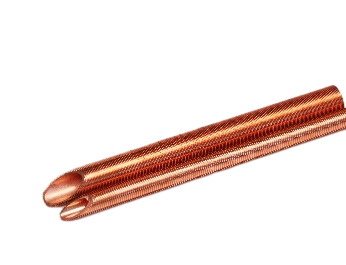
A low fin tube is a type of heat exchanger tube characterized by shallow, spiral fins along its outer surface. These fins increase the tube’s surface area, enhancing its ability to transfer heat between fluids. The fins on a low fin tube are typically 0.05 to 0.25 inches (1.3 to 6.4 mm) high, making them “low” compared to high fin or extended fin tubes.
The finned design improves heat exchange performance without significantly increasing the tube’s volume, allowing for efficient heat transfer in compact systems. Low fin tubes are commonly used in shell-and-tube heat exchangers, where they improve heat transfer rates between liquids and gases in industries such as petrochemical, power generation, and HVAC.
Benefits of Using Low Fin Tubes
Low fin tubes offer several advantages, making them popular in various heat exchange applications. Here’s why they are a preferred choice:
1. Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
The primary advantage of low fin tubes is their increased surface area, which allows for better heat transfer. The fins enhance the efficiency of the heat exchanger by allowing more contact between the tube surface and the surrounding fluid, improving the overall heat exchange rate.
2. Compact and Space-Saving Design
Compared to standard smooth tubes, low fin tubes can achieve the same heat transfer performance in a smaller space. This makes them ideal for compact applications, such as refrigeration units or HVAC systems, where space is limited.
3. Lower Material and Energy Costs
Because low fin tubes increase heat transfer efficiency, they often require fewer tubes or smaller exchangers to achieve the same level of performance. This reduction in materials and energy use can result in cost savings, making low fin tubes a more economical choice for both initial installation and long-term operation.
4. Durability in Various Applications
Low fin tubes are made from durable materials like copper, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys, making them resistant to corrosion, erosion, and high temperatures. This durability ensures that they perform effectively even in harsh industrial environments, such as chemical plants or refineries.
Key Applications of Low Fin Tubes
Low fin tubes are versatile and can be found in several industries where efficient heat transfer is critical. Here are some common applications:
1. Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers
In shell-and-tube heat exchangers, low fin tubes help enhance heat transfer between the shell and the tube-side fluids. By increasing the tube surface area, low fin tubes allow for efficient thermal exchange, making them widely used in applications like power plants, refineries, and chemical processing facilities.
2. Refrigeration and HVAC Systems
Low fin tubes are ideal for compact refrigeration units and HVAC systems, where space-saving designs are crucial. The increased heat transfer efficiency allows these systems to maintain desired temperatures without requiring large equipment, making them suitable for commercial and industrial refrigeration as well as residential air conditioning systems.
3. Oil and Gas Processing
In the oil and gas industry, low fin tubes are used in heat exchangers to cool and condense fluids efficiently. Their durability and resistance to harsh environments make them suitable for handling petrochemical fluids and high-pressure gas streams, which are common in oil refineries and gas processing plants.
Key Factors to Consider When Purchasing Low Fin Tubes
When selecting low fin tubes for your application, several factors can influence performance, cost, and longevity. Here’s a closer look at the most important considerations for purchasers:

1. Material Selection
The material of the low fin tube is crucial, as it determines the tube’s thermal conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. Common materials for low fin tubes include:
- Copper: Known for excellent thermal conductivity, copper is often used in HVAC and refrigeration systems for efficient heat transfer.
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion and high temperatures, stainless steel is ideal for industrial applications involving aggressive chemicals or high-pressure conditions.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is commonly used in automotive and air conditioning applications where weight is a factor.
Selecting the appropriate material depends on the operating environment, fluid characteristics, and durability requirements of your application.
2. Fin Density and Height
Fin density and height impact heat transfer efficiency and fluid flow resistance. For instance, higher fin densities offer more surface area but may increase pressure drop, while lower fin densities provide a smoother fluid flow but less surface area for heat transfer.
- High Fin Density: Increases heat transfer efficiency but may require higher energy to overcome pressure drops. This is suitable for high-efficiency applications with controlled flow rates.
- Low Fin Density: Reduces pressure drop but offers slightly lower heat transfer efficiency. Ideal for applications where fluid flow needs to be less restricted.
Choosing the right balance of fin density and height depends on your system’s heat transfer and pressure requirements.
3. Tube Dimensions
The outer diameter and wall thickness of the tube are also important factors, as they affect the overall efficiency and durability of the heat exchanger.
- Outer Diameter: Larger diameters increase the surface area but may require more space, making them suitable for larger installations.
- Wall Thickness: Thicker walls enhance durability but may slightly reduce heat transfer efficiency. Thinner walls are ideal for applications where space is limited and rapid heat transfer is essential.
Selecting the right dimensions ensures that the low fin tubes will fit well within your system and perform as expected under operating conditions.

4. Cost and Budget Considerations
Low fin tubes vary in price based on material, dimensions, and manufacturer. While copper and aluminum tubes are often more affordable, stainless steel and specialty alloys can be more expensive but offer greater durability. Balance cost with performance needs to ensure that you’re making a cost-effective choice without sacrificing quality.
Additionally, consider the long-term operating costs, as more efficient heat transfer may lead to energy savings over time.
5. Supplier Reputation and Quality Standards
Purchasing from a reputable supplier is essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of your low fin tubes. Look for suppliers that adhere to industry standards (such as ASME or ASTM) and provide consistent quality control. Choosing a trusted supplier can reduce risks associated with equipment failure, leading to fewer maintenance issues and downtime.
Maintenance Tips for Low Fin Tubes
Proper maintenance is crucial to maximize the lifespan and performance of low fin tubes. Here are a few tips to keep them operating efficiently:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust, dirt, and scale can accumulate on the fins, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Clean the fins and tubes regularly to maintain performance.
- Inspect for Corrosion: Depending on the environment, low fin tubes can experience corrosion over time. Regular inspections and timely treatment can prevent significant damage.
- Check for Leaks: Small leaks can impact efficiency and lead to costly repairs. Monitor for leaks, particularly if the tubes are used in high-pressure applications, and address them promptly.
Final Thoughts
Low fin tubes are efficient, compact, and versatile components in many heat exchange applications, offering enhanced heat transfer performance in a smaller form factor. By understanding their benefits and evaluating critical factors like material, fin density, and tube dimensions, buyers can select the right low fin tubes for their specific needs.
Summary: Low fin tubes feature shallow, spiral fins that increase surface area, improving heat transfer efficiency in compact systems. They are widely used in shell-and-tube heat exchangers, HVAC, refrigeration, and oil and gas industries. Key buying factors include material selection, fin density, tube dimensions, and supplier quality.
Purchasing the right low fin tubes for your application ensures effective heat transfer, reduced operating costs, and reliable performance over the long term.