Radiators play a critical role in heat exchange systems, from automotive engines to industrial equipment and HVAC systems. The tubes and fins of a radiator are its most important components, working together to ensure efficient heat transfer and optimal performance. This article delves into the purpose of these components, how they function, and why they’re essential to a radiator’s effectiveness. Whether you’re an engineer, technician, or someone looking to optimize your system, this guide provides the insights you need.
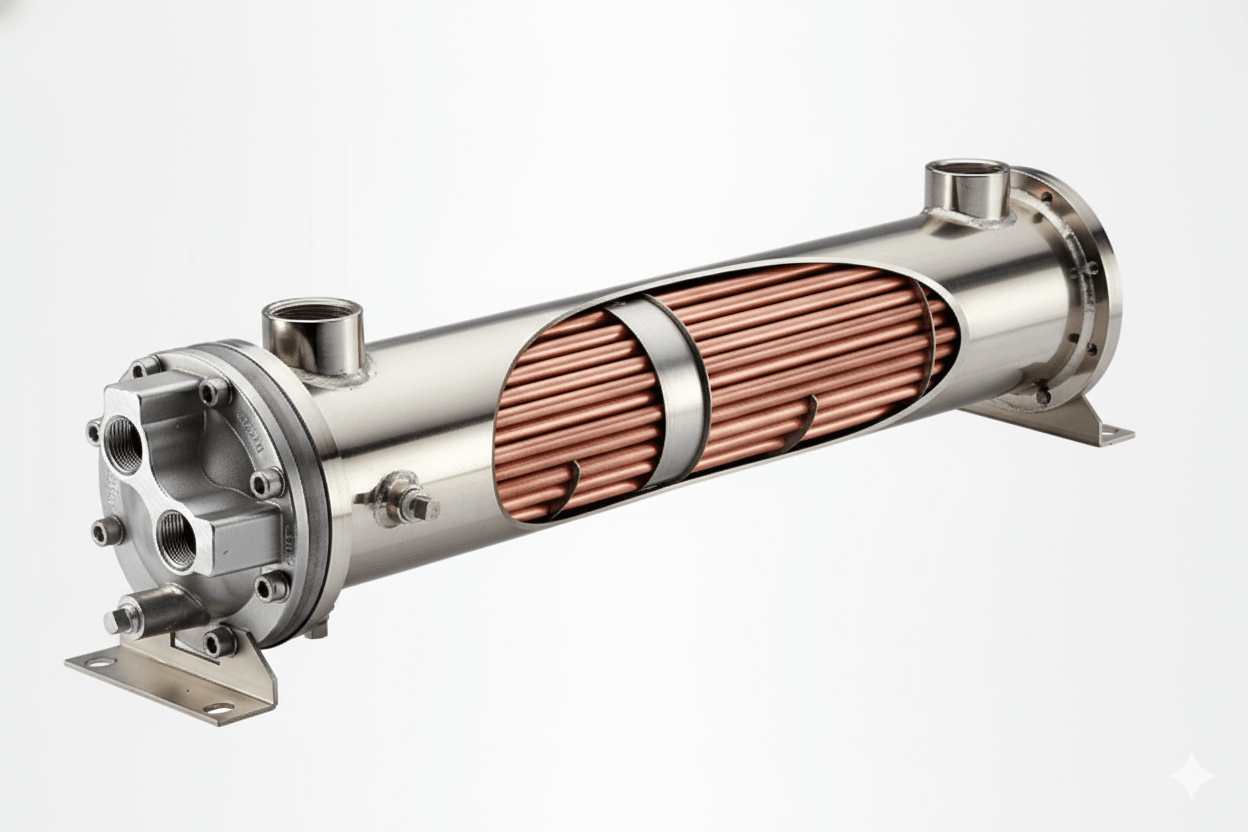
The tubes and fins of a radiator work together to transfer heat efficiently. Tubes carry the hot fluid, while fins increase the surface area to dissipate heat into the surrounding air. This combination maximizes cooling performance, ensuring the radiator maintains a consistent temperature.
The Role of Tubes in a Radiator
Tubes in a radiator serve as the primary channel for transporting hot fluid, such as coolant in automotive systems or steam in industrial applications. Here’s a closer look at their key purposes:
- Heat Conduction: The tubes absorb heat from the fluid as it flows through them. Materials like copper or aluminum, which have high thermal conductivity, are commonly used to enhance heat transfer.
- Fluid Transport: The tubes ensure a continuous flow of the heated liquid or gas, allowing the system to regulate temperatures effectively.
- Structural Integrity: In addition to their thermal role, the tubes provide durability and structural support to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
Tubes are often designed in various shapes—round, oval, or flat—depending on the application. Flat tubes are particularly common in modern radiators, as they offer a larger contact area for heat transfer without increasing the radiator’s size.
The Role of Fins in a Radiator
Fins in a radiator significantly enhance the system’s ability to dissipate heat. By extending outward from the tubes, they create more surface area for heat exchange with the air. Here’s why fins are indispensable:
- Increased Surface Area: The primary function of fins is to maximize the area exposed to airflow, which is critical for dissipating heat quickly.
- Airflow Optimization: Fins are strategically arranged to allow air to flow through the radiator, carrying heat away efficiently.
- Lightweight Design: Despite their effectiveness, fins are typically thin and lightweight, ensuring the radiator remains compact and easy to install.
Materials like aluminum are commonly used for fins because of their excellent thermal properties and resistance to corrosion. The spacing, shape, and design of the fins are optimized based on the radiator’s application to balance performance and cost.
How Tubes and Fins Work Together
The synergy between tubes and fins is what makes radiators so efficient. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how these components work together:
- Heat Absorption: The hot fluid flows through the tubes, transferring heat to the tube walls.
- Heat Transfer to Fins: The tubes conduct heat to the attached fins, which spread it across a larger surface area.
- Air-Cooling Process: As air moves across the fins—either naturally or with the help of a fan—the heat is dissipated into the surrounding environment.
- Temperature Regulation: This process continuously cools the fluid in the radiator, ensuring the entire system operates within a safe temperature range.
Without fins, the heat transfer would be limited to the surface of the tubes, significantly reducing the radiator’s efficiency. Similarly, without tubes to carry the fluid, the fins would lack a heat source to dissipate.
Applications of Tube-and-Fin Radiators
Tube-and-fin radiators are versatile and used in various industries:
- Automotive: Radiators in cars, trucks, and motorcycles rely on tubes and fins to cool engine coolant and maintain optimal engine temperatures.
- HVAC Systems: In heating and cooling systems, finned tube radiators regulate indoor temperatures by efficiently transferring heat.
- Industrial Equipment: From power plants to manufacturing facilities, these radiators cool steam or process fluids to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Electronics: High-performance computers and other electronic devices use miniaturized versions of tube-and-fin designs for thermal management.
Challenges and Solutions in Tube-and-Fin Radiators
Despite their efficiency, tube-and-fin radiators face certain challenges. Here’s how they’re addressed:
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture or certain chemicals can corrode the tubes or fins. Using corrosion-resistant materials like copper or aluminum and applying protective coatings can extend the radiator’s lifespan.
- Airflow Blockage: Dust and debris can accumulate on fins, reducing airflow and cooling efficiency. Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial.
- Pressure Loss: High fluid velocities can lead to pressure drops within the tubes. Optimized tube design and proper flow management ensure consistent performance.
- Mechanical Stress: Vibrations or thermal expansion can damage the connections between tubes and fins. Advanced welding or brazing techniques provide robust joint strength.
Innovations in Tube-and-Fin Technology
Modern radiators are evolving to meet the demands of more efficient and compact designs. Some innovations include:
- Microchannel Technology: Using smaller tubes with more closely packed fins to enhance heat transfer while reducing size and weight.
- Hybrid Materials: Combining materials like aluminum and composite polymers to balance thermal performance with cost savings.
- Improved Coatings: Advanced coatings not only protect against corrosion but also improve heat transfer rates by reducing surface resistance.
Tips for Optimizing Radiator Performance
To get the most out of a tube-and-fin radiator, follow these best practices:
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the fins and inspect the tubes for damage or leaks to ensure consistent performance.
- Optimal Placement: Install the radiator in a location with adequate airflow to maximize heat dissipation.
- Use the Right Coolant: For systems that use fluids, ensure the coolant is compatible with the radiator materials to prevent corrosion or scaling.
- Upgrade When Necessary: If your system operates in extreme conditions, consider upgrading to advanced designs with higher efficiency ratings.
Final Thoughts
The tubes and fins of a radiator are its heart and soul, working in tandem to ensure effective heat transfer. Tubes transport the hot fluid while fins amplify the cooling process by increasing surface area. Together, they make radiators indispensable in countless applications, from keeping your car engine cool to regulating temperatures in industrial equipment.
By understanding how tubes and fins function, you can make smarter choices about radiator selection, maintenance, and upgrades, ensuring your system operates efficiently and reliably for years to come. Whether you’re optimizing a system for performance or looking to solve cooling challenges, the science behind tube-and-fin radiators offers tried-and-true solutions.