When it comes to large-scale industrial applications, selecting the right heat exchanger is crucial for ensuring optimal heat transfer efficiency and minimizing operational costs. Two of the most commonly used heat exchangers in such applications are shell and tube heat exchangers and finned tube heat exchangers. While finned tubes are often favored in smaller or specialized systems, shell and tube heat exchangers tend to offer superior performance in large-scale applications. But why is this the case? Let’s dive deeper into the advantages of using shell and tube heat exchangers over finned tubes in larger, more demanding environments.
Understanding Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
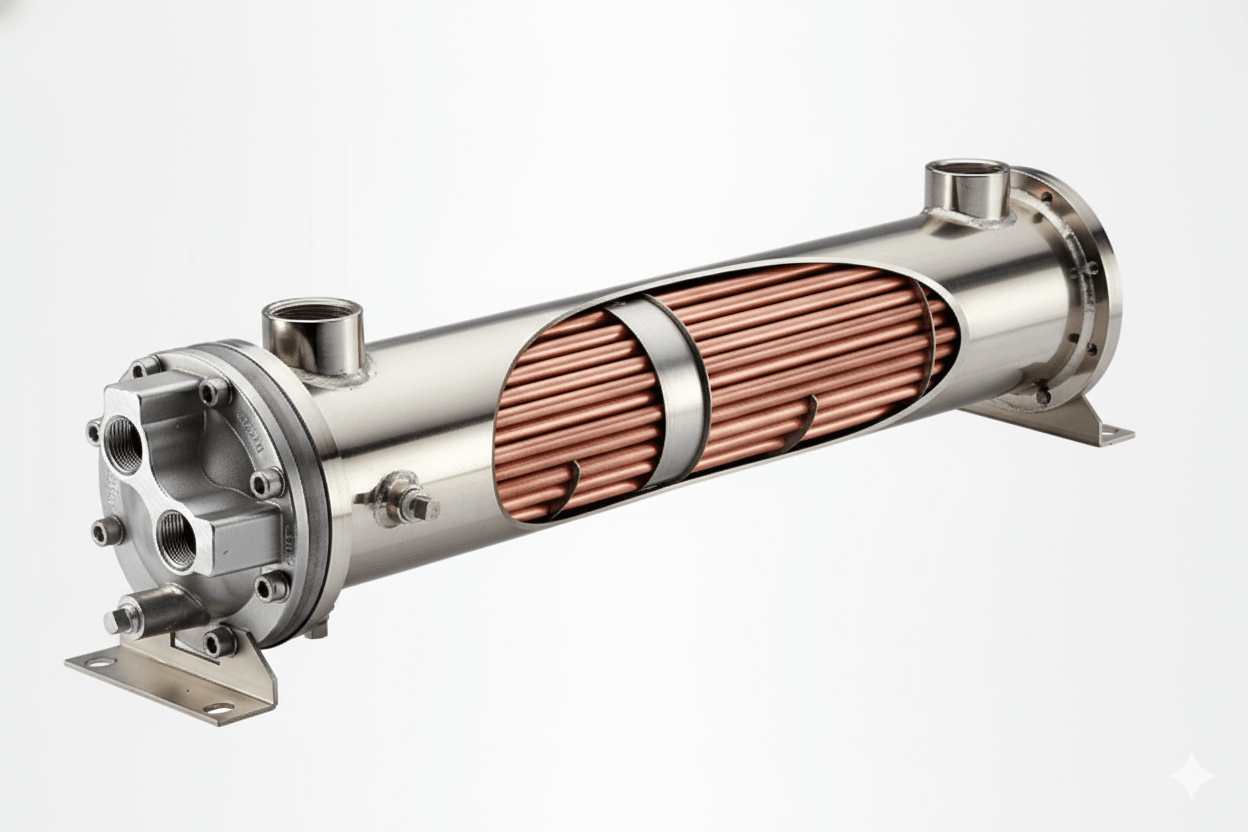
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other carrying the cold fluid. The tubes are arranged inside a cylindrical shell, with the fluids passing through the tubes and the shell-side, allowing heat to transfer between the two. This type of heat exchanger is commonly used in industries such as oil refining, power generation, and chemical processing.
The Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers in Large-Scale Applications
- Higher Heat Transfer Efficiency Shell and tube heat exchangers are designed to handle large volumes of fluid, making them more efficient for high heat loads. The design allows for better heat transfer rates because the flow of fluids on the tube side can be optimized for maximum heat exchange. In contrast, finned tube heat exchangers, while effective for heat exchange in air-cooled systems, struggle to match the efficiency of shell and tube exchangers when dealing with high heat capacities required in large-scale systems.
In shell and tube heat exchangers, the heat transfer surface area can be significantly increased by using smaller diameter tubes and arranging them more densely inside the shell. This allows for more effective heat exchange, particularly in systems that handle large amounts of hot and cold fluids simultaneously. Finned tubes, on the other hand, generally operate best in applications where a lower heat load is involved.
- Ability to Handle Higher Pressures In many large-scale industrial applications, fluids are pumped at high pressures. Shell and tube heat exchangers excel in these scenarios because they can be designed to withstand high-pressure environments. The tube arrangement inside the shell is sturdy, and the design can be customized to handle both high-pressure liquids and gases. This makes them ideal for industries like petrochemical and power plants, where pressure demands are often extreme.
Finned tubes, on the other hand, are typically used in lower-pressure applications due to their design and material limitations. The thin walls of the fins and the tubes themselves might not withstand the same pressure levels as those in shell and tube exchangers. This limits the range of applications where finned tubes can be used effectively.
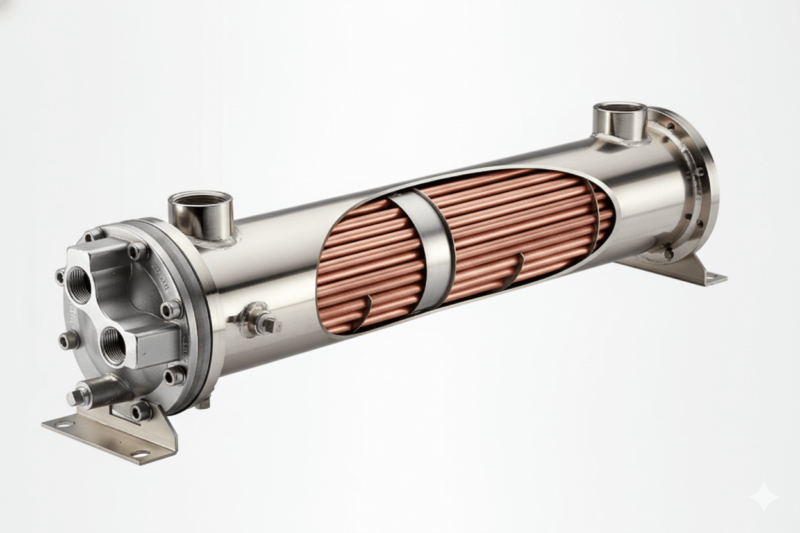
- Flexibility in Materials Shell and tube heat exchangers offer a high degree of flexibility in terms of materials. The tubes can be made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, titanium, copper, and alloys that are resistant to corrosion, high temperatures, and pressure. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of fluids, from corrosive chemicals to high-temperature oils and gases.
Finned tubes, while versatile for air-to-liquid heat exchange, are often limited in the materials available due to their exposure to external environmental factors. They are generally more prone to corrosion and wear when exposed to harsh industrial fluids. In applications where high chemical resistance or durability is needed, shell and tube heat exchangers have a clear advantage.
- Better Maintenance and Cleaning One of the standout advantages of shell and tube heat exchangers is the ease with which they can be maintained and cleaned. In large-scale applications, these heat exchangers are typically designed to be disassembled, which allows for easy access to the tubes for inspection and cleaning. Tube bundles can be removed and cleaned individually, which is crucial in industries where scaling or fouling is a concern.
Finned tube heat exchangers, however, are more difficult to clean effectively. The fins can accumulate debris, dust, and even biological growth, especially when used in air-cooled systems, which can reduce their heat transfer efficiency. The intricate fin structure makes it harder to remove blockages, and cleaning requires more effort and specialized equipment. For industries dealing with heavy fouling or scaling, shell and tube heat exchangers are often the better choice.
- Enhanced Durability and Longevity Shell and tube heat exchangers are built to last, especially when designed with corrosion-resistant materials. Their robust construction allows them to endure harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures, high pressures, and exposure to corrosive chemicals. They are less susceptible to physical damage compared to finned tubes, which can be prone to bending or damage under pressure.
The durability of shell and tube exchangers makes them ideal for industries that rely on continuous, long-term operation, such as power plants or chemical processing plants. Finned tube exchangers, though durable, may require more frequent replacement or maintenance in environments with harsh conditions.
- Scalability for Large-Scale Systems Shell and tube heat exchangers are highly scalable. As industrial applications grow and require more heat transfer capacity, shell and tube exchangers can be easily modified or expanded to meet increasing demand. Additional tube bundles can be added, or the shell can be made larger, providing a straightforward path for scaling up operations. This scalability makes them highly suitable for industries that need to increase production or heat exchange capacity over time.
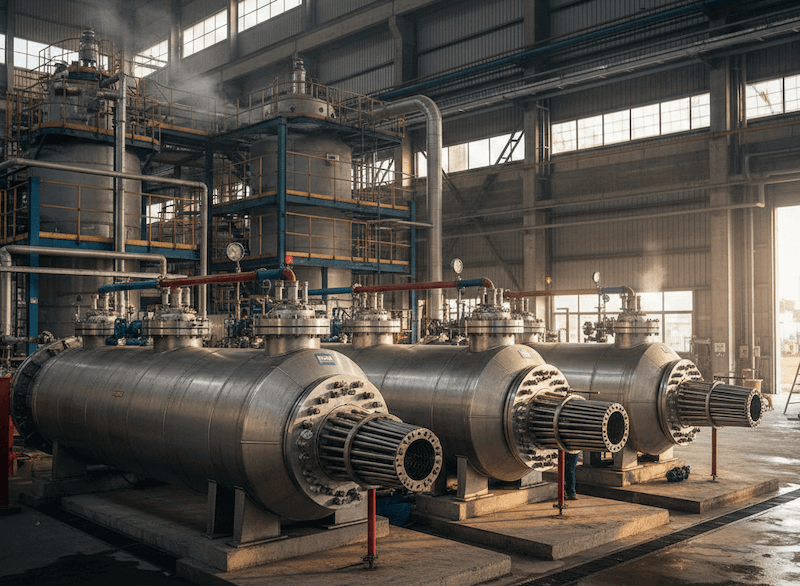
Finned tubes, however, have limitations when it comes to scaling up. While they are efficient for smaller systems, their design does not lend itself well to large-scale applications where massive heat transfer surface areas are required. As a result, shell and tube heat exchangers are often the go-to solution for industries looking to expand their heat exchange capacity.
When to Choose Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are ideal for large-scale applications where high heat transfer efficiency, durability, and the ability to handle high pressures are critical. Industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and HVAC systems rely on these exchangers for their ability to handle large volumes of fluids and withstand extreme operating conditions.
While finned tube heat exchangers have their place in smaller or air-based applications, shell and tube designs are better suited for large-scale industrial operations that require flexibility, maintenance ease, and the ability to scale as needed.
Conclusion
In large-scale applications, shell and tube heat exchangers offer a host of advantages over finned tubes, including superior heat transfer efficiency, the ability to withstand higher pressures, material flexibility, ease of maintenance, enhanced durability, and scalability. Their robust design and capacity to handle demanding industrial environments make them the go-to solution for many industries.
For large-scale systems, the shell and tube heat exchanger remains the most efficient and reliable choice, delivering unmatched performance in terms of heat transfer, durability, and ease of maintenance. Whether you are dealing with high temperatures, high pressures, or corrosive fluids, shell and tube heat exchangers provide a versatile and long-lasting solution that ensures the reliability and efficiency of your operations.