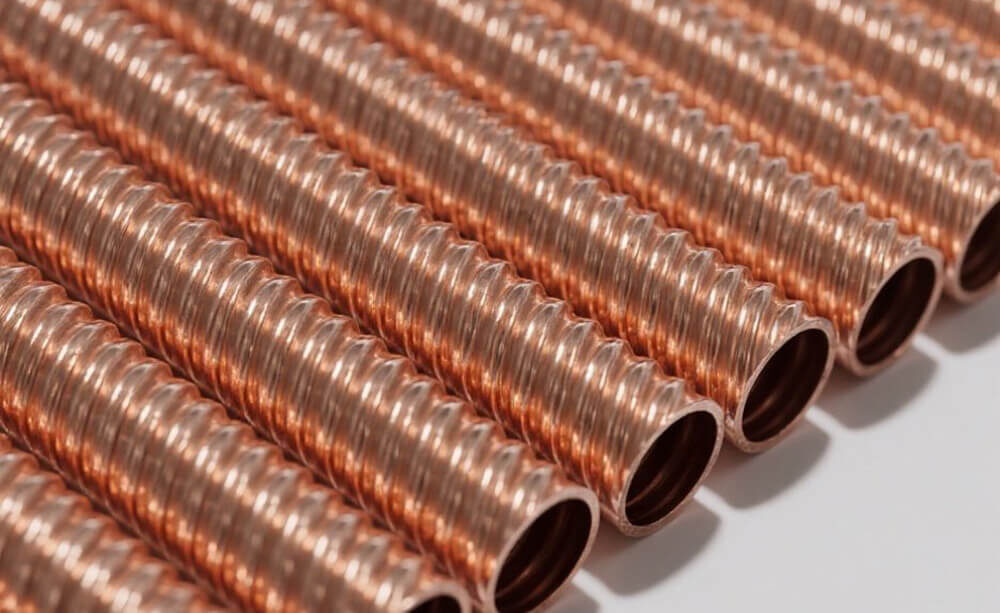
Finned tubes are a critical component in heat exchangers, helping industries improve heat transfer by increasing the surface area of the tubes. They’re used in various applications like HVAC systems, automotive radiators, and industrial processes, including oil and gas. There are two primary types of finned tubes: wrap-on finned tubes and embedded finned tubes. Although both serve the same basic purpose—improving heat transfer—their designs and performance vary significantly.
In this post, we’ll break down the differences between these two types of finned tubes, explore their advantages, and help you understand which one might be the best fit for your needs.
What Are Finned Tubes?
Before diving into the differences, let’s define what finned tubes are. A finned tube consists of a tube (typically made of copper, steel, or aluminum) with fins attached to its surface. The fins increase the surface area, allowing more heat to transfer between the fluid inside the tube and the surrounding air or another fluid. This makes heat exchangers much more efficient, as they can transfer more heat without needing to use a larger, bulkier system.
Now, let’s compare wrap-on and embedded finned tubes in detail.
Wrap-on Finned Tubes
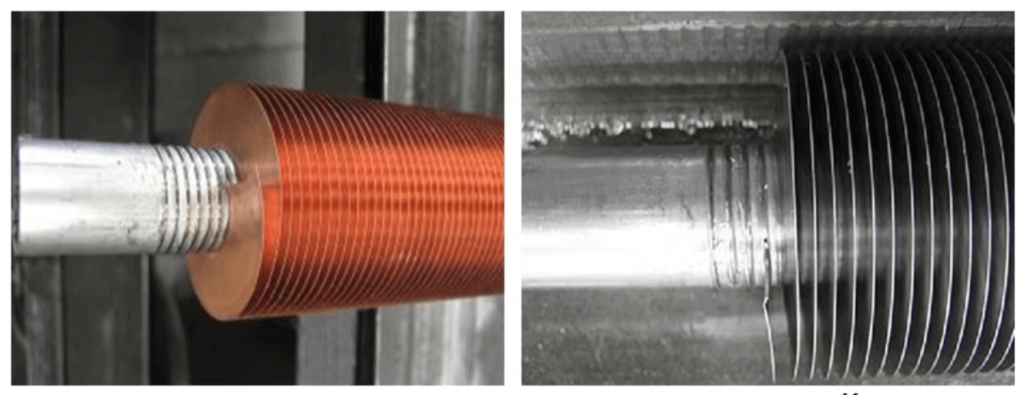
As the name suggests, wrap-on finned tubes have fins that are wrapped around the outside of the tube. These fins are typically made of aluminum, and they are wound in a helical pattern around the tube. The fins are held in place by the tension created when they are wrapped around the tube.
Advantages of Wrap-on Finned Tubes:
- Lower Cost
Wrap-on fins are cheaper to produce because the manufacturing process is simpler. The wrapping technique requires less precision than the embedded method, making these tubes a more affordable option for many applications. - Faster Production
Since the production process is simpler, wrap-on finned tubes can be made more quickly, which is beneficial for projects that require large quantities of tubes in a short time. - Ease of Replacement
If the fins get damaged or wear out over time, they can be replaced without much difficulty. The fins are wrapped loosely around the tube, so swapping them out is usually straightforward.
Disadvantages of Wrap-on Finned Tubes:
- Lower Heat Transfer Efficiency
Because the fins are simply wrapped around the tube, the contact between the fin and the tube may not be as efficient. This can result in slightly lower heat transfer performance compared to embedded designs. - Less Durability
The wrapping process means that the fins are more likely to loosen or be damaged under high pressure, vibration, or extreme temperatures, leading to reduced efficiency over time.
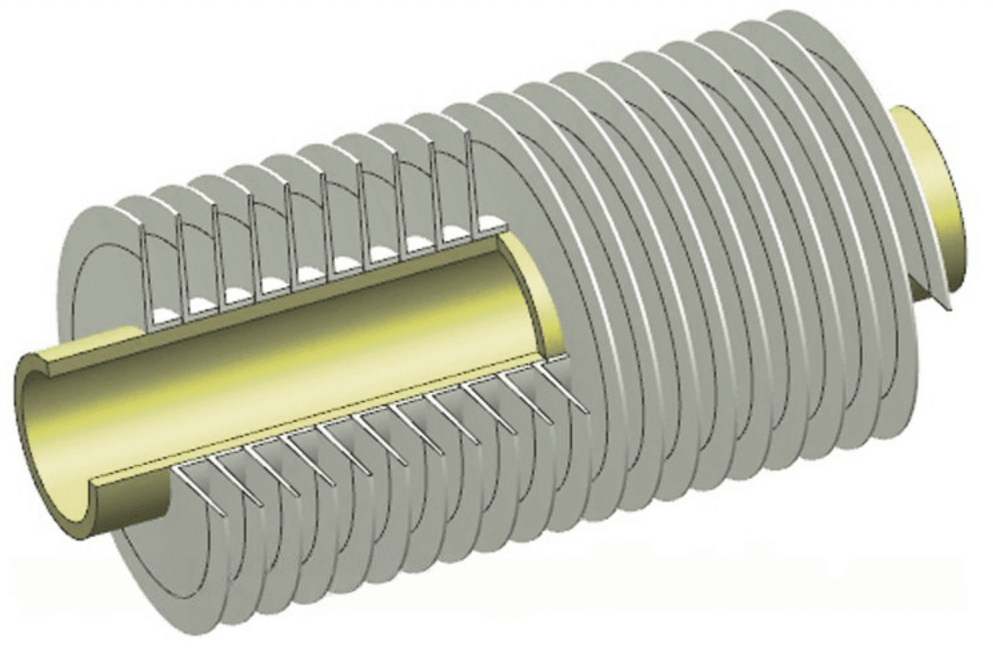
Embedded Finned Tubes
Embedded finned tubes differ in that the fins are integrated into the tube itself, often by extruding or bonding them during the manufacturing process. The fins can be made from the same material as the tube, such as copper or steel, ensuring a more robust and permanent bond.
Advantages of Embedded Finned Tubes:
- Higher Heat Transfer Efficiency
Because the fins are securely attached to the tube, the heat transfer efficiency is significantly better. The bond between the tube and the fins ensures a more seamless flow of heat, making these tubes ideal for high-performance applications. - Increased Durability
The embedded design makes these tubes much more resistant to damage. Whether exposed to high pressure, extreme temperatures, or vibrations, embedded finned tubes are more likely to maintain their integrity over time, providing long-lasting performance. - Better for Harsh Environments
Embedded finned tubes can withstand harsher environments, making them suitable for high-temperature industrial applications such as in oil refineries, power plants, and chemical plants.
Disadvantages of Embedded Finned Tubes:
- Higher Cost
Due to the more complex manufacturing process, embedded finned tubes are more expensive. The extrusion or bonding process requires more precision and advanced technology, making these tubes a more costly option. - Slower Production
Since the process is more intricate, it takes longer to manufacture embedded finned tubes. This can be a disadvantage if you need large quantities or have time constraints.
Key Differences Between Wrap-on and Embedded Finned Tubes
| Feature | Wrap-on Finned Tubes | Embedded Finned Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Simple wrapping of fins around the tube. | Fins are integrated into the tube during manufacturing. |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simple production. | Higher cost due to complex production. |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Lower efficiency compared to embedded tubes. | Superior heat transfer due to better fin-to-tube contact. |
| Durability | Less durable, fins can loosen or get damaged. | More durable, fins are tightly integrated into the tube. |
| Best Applications | Moderate heat transfer needs, cost-sensitive applications. | High-performance applications, high heat loads, harsh environments. |
Which Type Should You Choose?
The choice between wrap-on and embedded finned tubes largely depends on your specific needs and budget.
- Choose Wrap-on Finned Tubes if:
- You need a cost-effective solution for moderate heat transfer.
- You’re working with applications that don’t require the highest efficiency.
- You need a large number of tubes quickly and at a lower cost.
- Choose Embedded Finned Tubes if:
- You require high heat transfer efficiency for critical applications.
- Your equipment will operate in harsh environments or under high stress (such as in oil and gas or power generation).
- Durability and longevity are top priorities for your project.
Conclusion
Finned tubes are essential in many heat transfer systems, and understanding the differences between wrap-on and embedded finned tubes can help you make an informed choice. Wrap-on finned tubes are ideal for budget-conscious applications where heat transfer efficiency is moderate, while embedded finned tubes provide superior performance and durability for demanding, high-efficiency systems. By assessing your specific requirements, you can select the best option that balances cost and performance for your application.